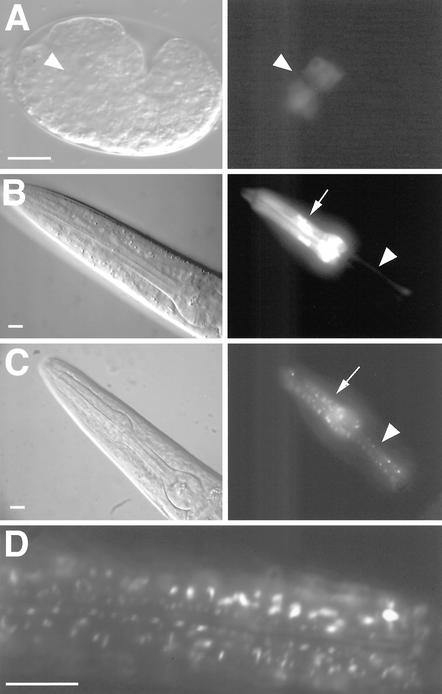
Figure 3.
inx-6 expression pattern during development. Differential interference contrast (left) and GFP fluorescence images (right) of transcriptional (inx-6::GFP) and translational (inx-6::INX-6::GFP) reporters. (A) Expression of the inx-6::GFP in embryo (anterior to the left) begins at the comma stage in anterior cells within the presumptive pharyngeal mesoderm (indicated by arrowhead). (B) inx-6::GFP is expressed in the corpus muscles (arrow) and isthmus marginal cells (arrowhead) throughout postembryonic development. (C) Expression of the inx-6::INX-6::GFP translational fusion reporter in a young adult hermaphrodite reveals a characteristic punctate expression pattern in corpus muscles (arrow) and isthmus marginal cells (arrowhead). The translational fusion construct fully rescued the mutant phenotype at 25°C, suggesting that the punctate GFP expression pattern may faithfully depict the expression of INX-6 in vivo. (D) A magnified image shows the punctate expression pattern in the corpus. Bars, 10 μm.