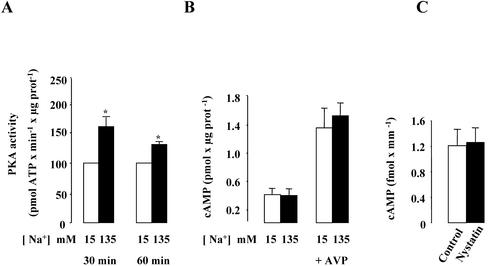
Figure 7.
Effect of high [Na+]i on PKA activity in mpkCCDc14 cells and cellular cAMP content in mpkCCDc14 cells and isolated rat CCDs. (A and B) Confluent mpkCCDcl4 cells grown on polycarbonate filters were first preincubated in the presence of 15 or 135 mM Na+ for 30 min at 37°C. (A) After permeabilization by 1 μg/ml amphotericin B, cells were incubated for 30–60 min at 37°C. The PKA activity was measured on homogenized cells using the SignaTECT cAMP-dependent Protein Kinase Assay System as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. Results expressed as pmol ATP × min–1 × μg protein–1 are means ± SE from four independent experiments. *p <0.05 vs. 15 mM Na+ values. (B) After permeabilization by 1 μg/ml amphotericin B, cells were incubated for 60 min at 37°C and 10–9 M vasopressin (AVP) was added or not to the cell medium during the last 10 min of incubation. The cellular cAMP content was measured on homogenized cells using the cyclic AMP (3H) assay system as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. Results expressed as pmol cAMP × μg protein–1 are means ± SE from four independent experiments. (C) Microdissected CCDs were incubated in the absence (control) or presence of 0.1 U/μl nystatin for 1 h at 37°C. Cellular cAMP content was determined using a radioimmunoassay as described in MATERIAL AND METHODS. Results expressed as fmol cAMP × mm–1 are means ± SE from six animals.