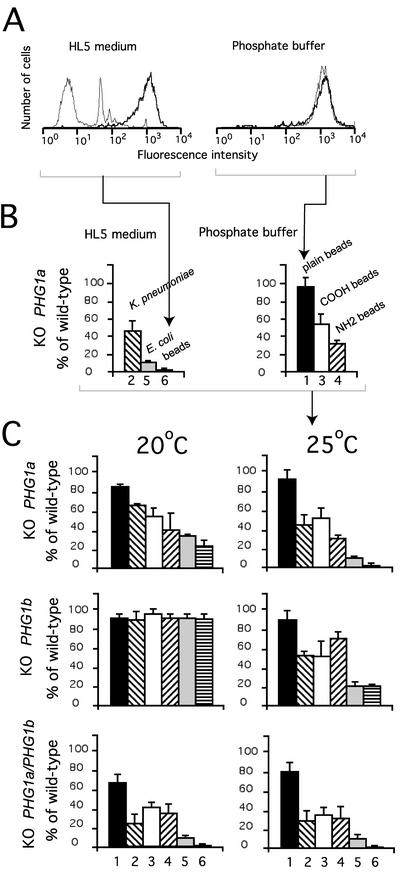
Figure 5.
PHG1 knockout cells display a similar phagocytosis defect. (A) Fluorescent-activated cell sorter analysis. Wild-type cells (thick lane) or PHG1a knockout cells (thin lane) were incubated for 20 min in the presence of fluorescent plain latex beads in HL5 or phosphate buffer at 25°C. The amount of internalized fluorescence was measured as relative fluorescence intensity. Arrowheads indicate the corresponding bar graph in B. (B) Phagocytosis rates of three substrates by PHG1a knockout cells were measured at 25°C in HL5 medium or phosphate buffer and expressed as percentage of wild-type cells: 1, plain latex beads in phosphate buffer (hydrophobic surface); 2, K. pneumoniae in HL5; 3, carboxylate (COOH)-substituted latex beads in phosphate buffer; 4, amino (NH2)-substituted latex beads in phosphate buffer; 5, E. coli in HL5; and 6, plain, carboxylate, or amino-latex beads in HL5 (hydrophilic surface). These data were combined in C to provide a general view of the phagocytosis defects in the different mutants. (C) Specificity of the phagocytosis defect observed for PHG1a, PHG1b, and PHG1a/PHG1b knockout cells at 20°C or 25°C is represented. These data represent the average of four independent experiments and the SD is indicated.