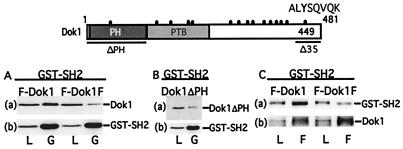
Figure 3.
Dok1 association with SH2D1A in vivo requires the Dok1 PH domain and Y449. A schematic diagram of Dok1 and the Dok1 mutations used in these experiments is shown above A–C. Dok1, Dok1 with a Y to F mutation at position 449 (Dok1F), Dok1 with C-terminal 35 amino acids deleted (Dok1ΔC35), and Dok1 with deletion of the PH domain (Dok1ΔPH) are represented. The relative positions of the PH domain and the phosphotyrosine binding (PTB) domain are indicated. Tyrosine residues are indicated by a filled circle. Y449 is indicated in bold in the context of the potential binding motif for SH2D1A. (A–C) Cos 7 cells were transfected with eukaryotic GST pEBG-base expression plasmid for SH2D1A (GST-SH2) in combination with pcDNA3-FLAG-Dok1 (F-Dok1), with pcDNA3-FLAG-Dok1Y449F (F-Dok1F) (A), or with pcDNA3-Dok1ΔPH (Dok1ΔPH) (B). At 48 h after transfection, cell lysates were incubated with glutathione beads and adsorbed proteins were analyzed by Western blotting with Dok1 (a) or GST-specific antibody (b). The positions of Dok1 and GST-SH2 are indicated. (C) The reciprocal experiment is shown with FLAG antibody immune precipitation followed by Western blotting with GST- (a) or αp-Y- (b) specific antibodies. The positions of Dok1 and GST-SH2 are indicated. L, 1% total lysate; G, glutathione bead precipitation; F, FLAG antibody immune precipitation.