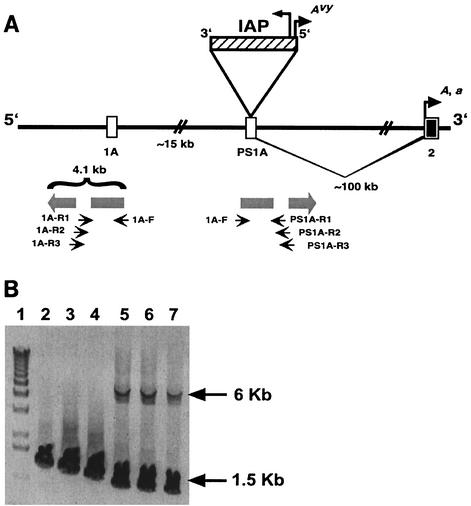
FIG. 1.
IAP insertion site in Avy allele. (A) Exon 1A of the murine agouti gene lies within an interrupted 4.1-kb inverted duplication (shaded block arrows). The duplication gave rise to pseudoexon 1A (PS1A). On the A allele, PS1A is located ≈100 kb upstream of exon 2 and ≈15 kb downstream of the contraoriented exon 1A (6). The Avy mutation was caused by a contraoriented IAP insertion (striped bar; tall arrowhead shows direction of IAP transcription). A cryptic promoter within the long terminal repeat proximal to the agouti gene (short arrowhead labeled Avy) drives ectopic agouti expression in Avy animals. In A and a animals, transcription starts from a hair cycle-specific promoter in exon 2 (short arrowhead labeled A, a). Small arrows show the positions of PCR primers used to selectively amplify the exon 1A and PS1A regions. (B) Agarose gel showing products of long-range PCR of Avy/a genomic DNA. Forward (F) and reverse (R) primers are described relative to the direction of the inverted duplicate regions and are shown in A. The same forward primer was used in all reactions. Three different reverse primers specific to the PS1A region (lanes 5 to 7) amplified fragments of ≈1.4 kb (the a allele) and ≈6 kb (the Avy allele, including the IAP insert). Three different reverse primers specific to the exon 1A region (lanes 2 to 4) amplified only the smaller fragments (≈1.6 kb). The exon 1A fragments are larger than the PS1A a fragments due to the more distal location of the exon 1A reverse primers.