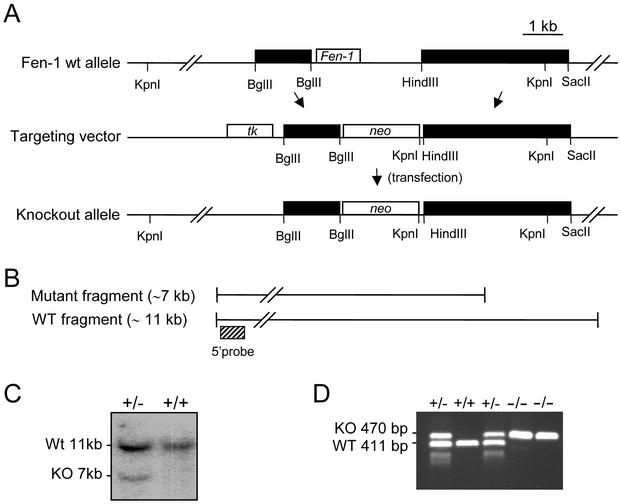
FIG. 1.
Targeted disruption of the murine Fen1 locus. (A) Physical map of the genomic DNA containing the Fen1 gene. Exon 2, containing the entire ORF of the Fen1 gene, is boxed. Genomic sequences, represented by solid boxes, were subcloned on either side of a neo gene, generating a targeting construct that deleted the entire Fen1 coding sequence. Murine genomic DNA is represented by solid boxes, vector sequences by a line, and Neo and Tk genes (positive and negative selection, respectively) by open boxes. (B) Restriction digest of genomic DNA by KpnI giving rise to an ∼11-kb fragment, using a 5′ flanking probe as indicated. A gene-targeted locus was detected by hybridization with an ∼7-kb fragment. (C) Southern blot analysis of ES cell lines. A positive, gene-targeted ES-cell line yields a 7-kb fragment in addition to the 11-kb wild-type (WT) fragment. KO, knockout. (D) PCR genotyping of DNA isolated from E3.5 blastocysts resulting from crossing of twoFen1+/− mice. A 411-bp wild-type band and a 470-bp mutant band were amplified with primer pairs P1-P2 and P1-P3. The locations and sequences for PCR primers are as described in Materials and Methods.