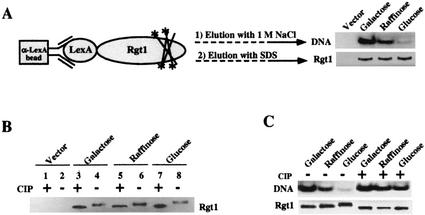
FIG. 9.
Glucose-induced phosphorylation inhibits DNA-binding activity of Rgt1 in vitro. (A) IDBA. LexA-Rgt1 was immunoprecipitated from yeast extracts as described in the legend to Fig. 7A and incubated with 32P-labeled DNA containing four Rgt1 binding sites (a repeat of Rgt1 binding sites C1 and C2). Approximately 85% of the DNA was bound to anti-LexA-Rgt1 beads. The bound DNA was eluted with 1 M NaCl. The Rgt1 bound to anti-LexA beads was subsequently eluted by boiling the beads in SDS buffer. The eluted DNA and Rgt1 were resolved in polyacrylamide gels and visualized by autoradiography and Western blotting (using anti-LexA antibody), respectively. (B) Rgt1 is phosphorylated. Rgt1 was immunoprecipitated as described above and incubated with (+) or without (−) 10 U of CIP at 37°C for 30 min and then subjected to Western blotting. (C) Glucose-induced phosphorylation of Rgt1 inhibits its DNA-binding activity. IDBA (DNA) and Western blotting (Rgt1) were performed on phosphorylated and dephosphorylated (CIP-treated) Rgt1 as for panels A and B.