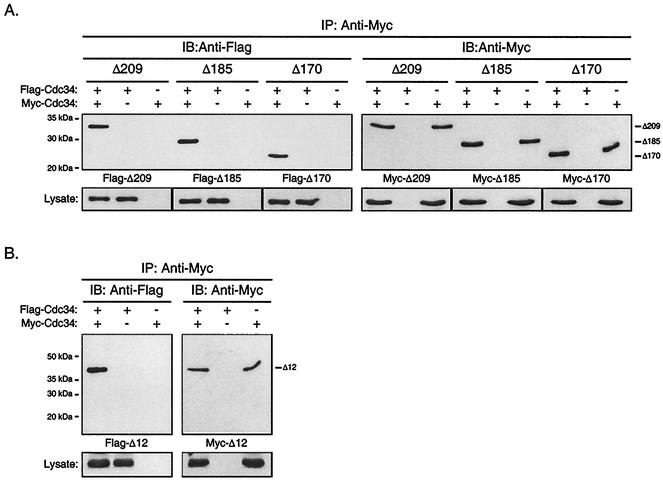
FIG. 2.
The Cdc34 carboxy-terminal extension and catalytic domain insertion are dispensable with respect to Cdc34 self-association. The same coimmunoprecipitation strategy as employed for Cdc34 (Fig. 1B) was employed for the Δ209 (residues 1 to 209), Δ185 (residues 1 to 185), and Δ170 (residues 1 to 170) carboxy-terminal truncation derivatives (A) as well as for the Δ12 (residues 103 to 114 deleted) catalytic domain deletion derivative (B). Flag- and Myc-tagged versions of these truncation derivatives were expressed in YPH499 cells. Cell lysates were extracted and subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with an anti-Myc antibody followed by immunoblotting (IB) with an anti-Myc antibody (right panels) and an anti-Flag antibody (left panels). Protein expression levels within the lysates used for immunoprecipitations are shown at the bottoms of the respective panels.