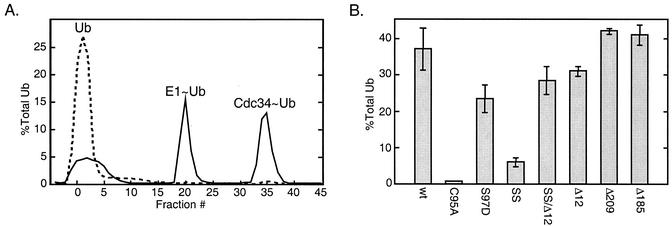
FIG. 5.
Ub thiolester formation. In vitro Ub thiolester formation was compared for a number of Cdc34 derivatives. Reaction mixtures containing Cdc34 or one of its derivatives (100 nM), Uba1 (10 nM), 35S-Ub (200 nM), and an ATP cocktail were incubated for 5 min at 30°C. Reactions were stopped by the addition of 50 mM EDTA, and the mixtures were then immediately loaded onto an anion-exchange column to separate reaction products. The Δ209 and Δ185 derivatives were separated by using a Superdex 75 HR10/30 size exclusion column (see Materials and Methods). (A) Example of the elution profile generated for a reaction mixture containing Cdc34 (solid line). Peaks containing 35S-Ub correspond to free Ub, Ub incorporated into Uba1 (E1∼Ub), and Cdc34 (Cdc34∼Ub) thiolester. In a separate reaction mixture, 10 mM DTT was added to disrupt thiolester (dashed line). (B) Incorporation of 35S-Ub into thiolester was determined for each Cdc34 derivative as a percentage of the total 35S-Ub added to each reaction mixture. The mean and standard deviation observed for three separate reactions for each derivative is shown. SS, S73K/S97D derivative; SSΔ12, S73K/S97D/Δ12 derivative; Δ12, catalytic domain insert deletion (residues 103 to 114 deleted); Δ209 and Δ185, carboxy-terminal truncation derivatives (residues 1 to 209 and 1 to 185, respectively).