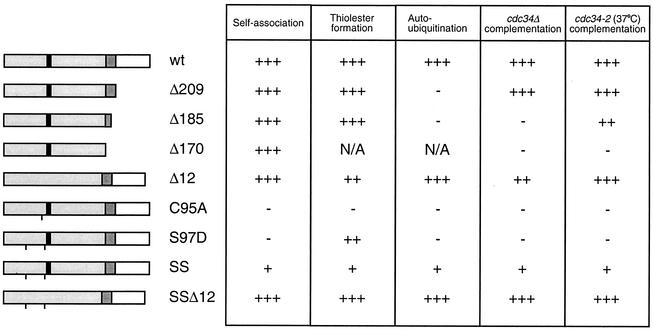
FIG. 8.
Functional comparison of the Cdc34 derivatives. The primary structures of various Cdc34 derivatives are shown, with the catalytic domain shown in light gray and the 12-amino-acid insert that is present within the catalytic domain shown in black (amino acids 103 to 114). The carboxy-terminal extension is shown in white, and residues of this domain previously shown to be necessary and sufficient for Cdc34 function are shown in dark gray (amino acids 170 to 209) (21). A line at the appropriate position along the block diagram indicates the position of the point substitution(s) present in each derivative. The various derivatives are scored based on their abilities to self-associate, form Cdc34∼Ub thiolester, build multi-Ub chains in an autoubiquitination reaction, and complement either a cdc34 disruption strain (cdc34Δ) or a cdc34(Ts) strain (cdc34-2) (3, 19, 26). Each derivative was scored relative to wild-type (wt) Cdc34 (+++) such that partial function was scored as ++ or + and the absence of function was scored as −. N/A, not applicable.