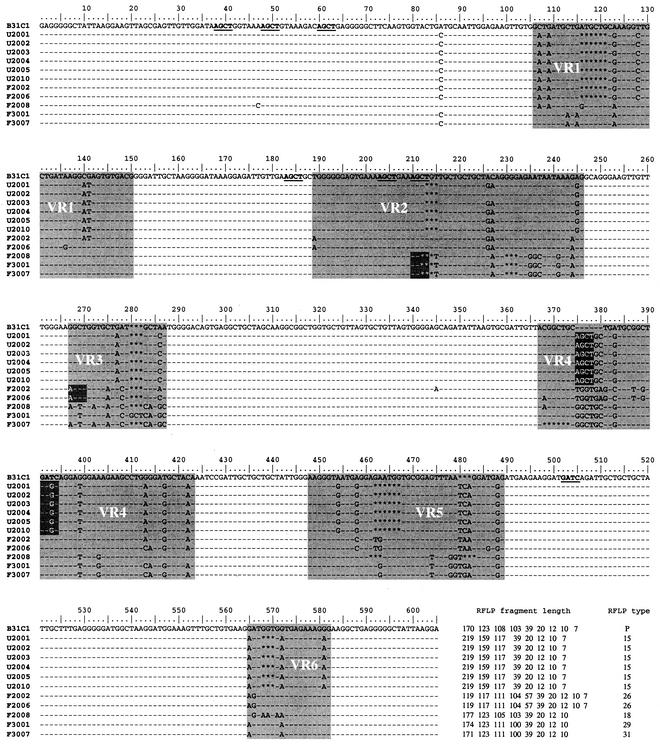
FIG. 3.
Validation of vlsE RFLP assay by DNA sequencing. Twelve clones with known RFLP patterns were sequenced. The clones were derived from cultured B31-C1 (1 clone), unfed nymphs (6 clones: U2001, U2002, U2003, U2004, U2005, and U2010), and partially fed nymphs (5 clones: F2002, F2006, F2008, F3001, and F3007). The sequences were aligned by using a multiple-alignment software, ClustalW, version 1.4. Nucleotides that are identical to the parental B31C1 strain are marked as dashes, and changes are indicated with the letter of the new nucleotide. Gaps are indicated by asterisks. AluI (AGCT) and MboI (GATC) sites on the B31C1 sequence are underlined. Nucleotide changes in the tick clones that lead to the creation or destruction of an AluI or MboI site are indicated in white text. The variable domain consists of six hypervariable regions, which are shaded and labeled VR1 to VR6. The expected fragment sizes for each clone following AluI and MboI digestion and the designated RFLP type are indicated at the end of the sequence.