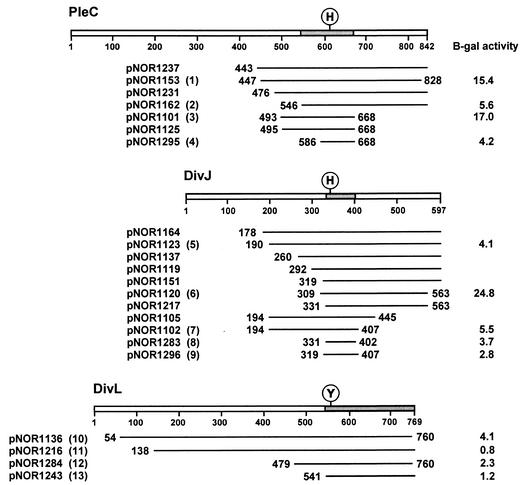
FIG. 1.
Polypeptide fragments of kinases DivJ, PleC, and DivL that interact with DivK in the yeast two-hybrid screen. An alignment of translated inserts in representative DivJ, PleC, and DivL clones is shown. The positions of the N- and C-terminal residues are indicated for each fragment, except those that extended to the C-terminal end of the proteins. Locations of the conserved sites of phosphorylation, histidine (H) in DivJ and PleC and tyrosine (Y) in DivL, are shown. Shaded areas of each kinase represent overlapping sequences common to the respective DivJ, PleC, and DivL clones. The numbers in parentheses following plasmid names identify the clones tested in the spot test shown in Fig. 3. β-Galactosidase (B-gal) assays (17) were performed on the cultures of the same clones that were grown in SC medium lacking leucine and uracil to mid-exponential phase. At least three independent cultures of each strain were assayed. Including the clones shown here, the fusion joints of 76 clones were sequenced. Among 34 pleC clones sequenced, the most frequent fusion points were either at amino acid 456 (7 clones) or between amino acids 492 and 495 (21 clones). Of the 42 DivJ clones sequenced, a total of 21 DivJ fragments started between residues 190 and 196 and 6 started between residues 328 and 331. The C-terminal ends of most clones were not sequenced.