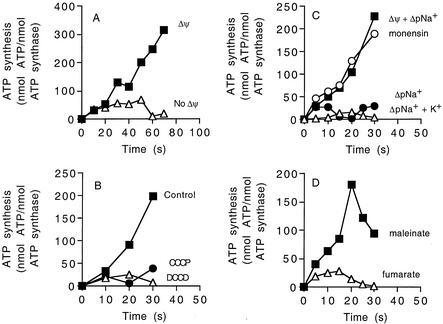
FIG. 5.
ATP synthesis by the reconstituted ATP synthase in proteoliposomes. (A) Proteoliposomes energized by a valinomycin-induced potassium diffusion potential applied in the absence of ΔpNa+ at 45°C. Valinomycin (2 μM) was added at 5 s to create a diffusion potential of 100 mV (▪). In another experiment no valinomycin was added (▵). (B) Effect of CCCP (10 μM) (•) or DCCD (20 μM) (▵) on ATP synthesis by proteoliposomes energized by a valinomycin-induced potassium diffusion potential applied in the absence of ΔpNa+. Inhibitors were preincubated with proteoliposomes for 5 min prior to addition of valinomycin (5 s). (C) Effect of ΔpNa+ on ATP synthesis by proteoliposomes. To start the reaction, sodium-loaded proteoliposomes (100 mM NaCl) were diluted 40-fold into one of the following buffers and ATP synthesis was determined as described in the text: 10 mM Tricine-KOH containing 2.5 mM NaCl (inside NaCl concentration, 100 mM) to generate a ΔpNa+ of 100 mV (•); 2.5 mM NaCl and approximately 200 mM KCl to generate a ΔpNa+ of 100 mV (▵); 2.5 mM NaCl and approximately 200 mM KCl and 2 μM valinomycin to generate a ΔpNa+ of 100 mV and a K+/valinomycin diffusion potential of 100 mV (▪); 5 μM monensin, 2.5 mM NaCl, 200 mM KCl, and 2 μM valinomycin to generate a ΔpNa+ of 100 mV and a K+/valinomycin diffusion potential of 100 mV (○). (D) ATP synthesis energized by Δp generated by either maleinate (▪) (ΔpH of 190 mV and Δψ of approximately 120 mV) or fumarate (▵) (ΔpH of 190 mV) (13). For all experiments, the values are the means of two to six independent determinations, and the experimental error associated with these values was less than 15%.