Figure 4.
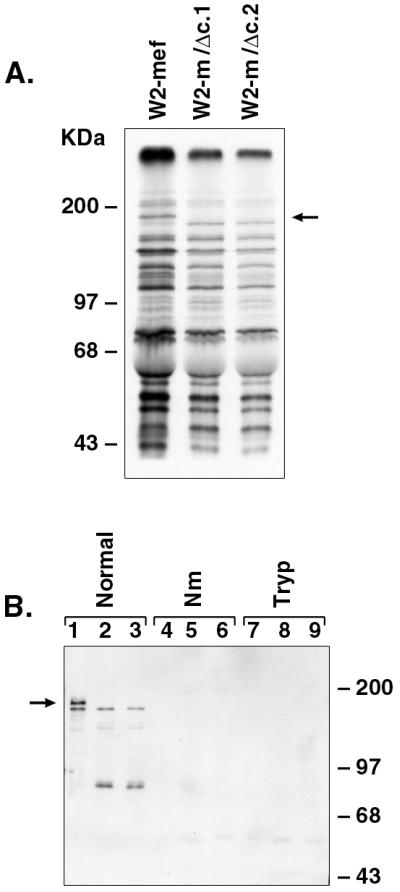
Erythrocyte binding assays of metabolically labeled parasite proteins. (A) Metabolically labeled culture supernatant proteins derived from merozoites released after schizont rupture were analyzed by SDS/PAGE (7%) and fluorography. The absence of wild-type EBA-175 within the culture supernatants obtained from W2-m/Δc.1 and W2-m/Δc.2 is indicated by an arrow. (B) Erythrocyte binding assays were carried out by incubating metabolically labeled parasite proteins present in culture supernatant with either normal, neuraminidase-treated (Nm), or trypsin-treated (Tryp) erythrocytes. After salt elution, labeled proteins were analyzed by Western blotting using αEBA-175 antibodies. Lanes 1–9 are as follows: W2-mef (lanes 1, 4, and 7), W2-m/Δc.1 (lanes 2, 5, and 8), W2-m/Δc.2 (lanes 3, 6, and 9). This result confirms that wild-type and truncated EBA-175 binds normal erythrocytes, although binding of truncated EBA-175 appears to be consistently less than that of the wild-type EBA-175. Neither wild-type nor truncated EBA-175 binds Nm- or trypsin-treated erythrocytes. Soybean trypsin inhibitor alone has no effect on protein binding (not shown). The arrow indicates the position of wild-type EBA-175.
