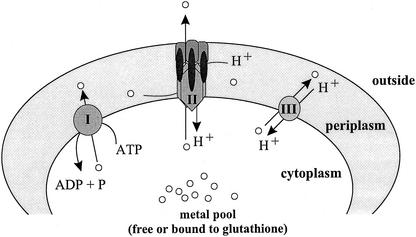
FIG. 1.
Prototypes of known efflux systems for zinc and cadmium in R. metallidurans. The Zn2+ and Cd2+ cations are exported from the cytoplasm (free or bound to thiols like glutathione) to the periplasm (grey area) by P-type ATPases (I) or by CDF (III) that are driven by the chemiosmotic gradient. The more complicated RND-driven efflux systems (II) are composed of an RND protein in the cytoplasmic membrane, an outer membrane factor, and a membrane fusion protein. Accordingly to the structures of the RND protein AcrB (21) and the outer membrane factor TolC (14), a trimeric state of all three subunits of the RND-driven efflux complex is assumed. CzcCBA is driven by the proton motive force (H+) (8, 23). The cationic substrates (white circles) may be directly exported out of the cell from the cytoplasm or periplasm (21).