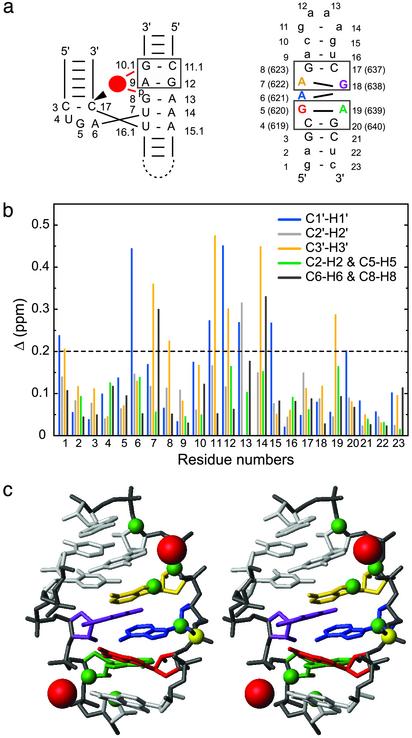
Fig. 4.
Mg2+ binding sites of SL1′.(a) Schematic comparing the 5′-A G-3′/5′-C G-3′ metal-ion binding motif (box) of the hammerhead ribozyme (Left) (36) and the two 5′-A G-3′/5′-C G-3′ motifs (boxes) in the internal loop of SL1′ (Right). For the hammerhead ribozyme, the bound Mg2+ is represented by a red circle, and the cleavage site is indicated by the arrowhead. (b) Chemical-shift changes (Δ in ppm ± 0.03 ppm; see Methods) after addition of 10 mM MgCl2 for the 1′, 2′, 3′, 6/8, and 2/5 proton and carbon atoms of all SL1′ residues. (c) Summary of Mg2+ binding data on the stereoview of the minimized average structure of SL1′ (residues C4-A9 and U16-G20). Significant chemical-shift changes after addition of 10 mM MgCl2 (Δ >0.2 ppm) were mapped as green spheres on the respective C1′, C2′, C3′, C6/C8, and C2/C5 atoms. Putative locations for the Mg2+ (red spheres) were obtained by heavy-atom superposition of the 5′-A G-3′/5′-C G-3′ motif from the x-ray structure of the Mg2+-bound hammerhead ribozyme (only Mg2+ are shown) (36) with the 5′-A639 G640-3′/5′-C619 G 620-3′ (rmsd of 1.01 Å) and the 5′-A622 G623-3′/5′-C637 G 638-3′ (rmsd of 1.56 Å) motifs from the minimized average structure of SL1′.