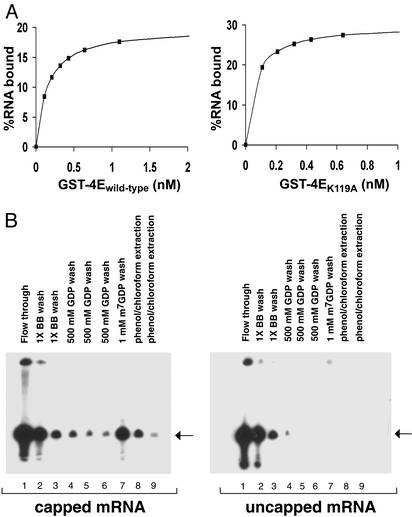
Fig. 1.
(A) Relative ability of GST-4Ewild-type and GST-4EK119A to bind 5′ capped mRNA. Batch mRNA-binding assays were performed to compare binding affinities of GST-4Ewild-type and GST-4EK119A. 5′ capped 32P-labeled mRNA was incubated in binding buffer with increasing amounts of GST-4Ewild-type and GST-4EK119A bound to agarose beads (see Materials and Methods). The quantity of mRNA bound to GST-4E agarose beads was measured by Cerenkov counts. The estimated dissociation constants (Kd) of GST-4Ewild-type and GST-4EK119A were 0.15 and 0.06 nM for capped mRNA, respectively. (B) Specificity of GST-4EK119A for 5′ capped mRNA. The batch purification of mRNA using GST-4EK119A was tested for its ability to bind both 5′ capped and uncapped mRNAs. Capped and uncapped mRNA synthesized in vitro using T7 polymerase were mixed with GST-4EK119A agarose beads (50 μl), washed with 1× binding buffer, 500 μM GDP, and eluted with 1 mM m7GDP (see Materials and Methods). mRNA that remained bound to GST-4E beads despite the m7GDP elution step was recovered by extraction with acid phenol/chloroform. mRNA isolated by using GST-4EK119A agarose beads are shown for purifications where 5′ capped (10–30%) and uncapped mRNA were used as starting material. mRNA present in each fraction was precipitated with ethanol and analyzed by 7 M urea/polyacrylamide (6%) gel electrophoresis and autoradiography. As determined by Cerenkov counts, the 1 mM m7GDP eluant (capped mRNA, lane 7) contained 85% of the total RNA recovered from the GST-4EK119A beads. The arrow indicates the size of the mRNA (50 nt) used as starting material.