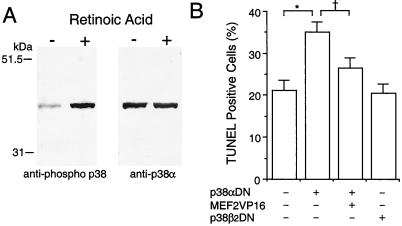
Figure 5.
Involvement of the p38α/MEF2 pathway in preventing apoptosis during neuronal differentiation of P19 cells. (A) p38α was phosphorylated during induction of neuronal differentiation by retinoic acid. Anti-phospho p38 was used to detect activated/phosphorylated p38 family members on immunoblots during induction of neuronal differentiation. The same membrane then was stripped and reblotted with a p38α-specific antibody that labeled the same band. (B) Dominant negative p38α (p38αDN) enhanced apoptosis during neuronal differentiation. Constitutively active MEF2C (MEF2VP16) significantly rescued the differentiating cells from apoptosis. Dominant negative p38β2 (p38β2DN) had no effect on apoptosis compared with control (expression vector only). After treatment with retinoic acid for 1 day, cells were transfected with the indicated expression vector(s) along with a GFP expression vector to identify the transfected cells. The number of transfected apoptotic cells was determined in a blinded fashion by TUNEL assay on day 3 of retinoic acid treatment. More than 1,200 GFP-positive cells were scored in each culture. Mean ± SD are shown from three experiments (*, P < 0.001; †, P < 0.01 by ANOVA and post hoc comparison).