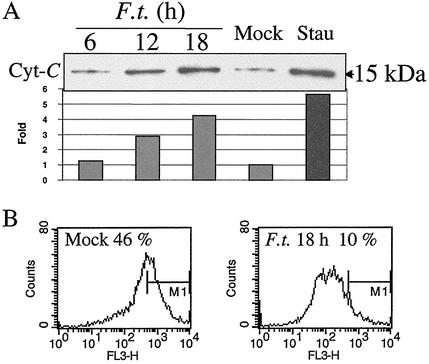
FIG. 1.
Release of cytochrome c and perturbation of the mitochondrial membrane potential in F. tularensis-infected J774A.1 macrophage cells. (A) Cytochrome c (Cyt-C) was enriched in cytoplasmic preparations from F. tularensis-infected J774A.1 macrophages. J774A.1 macrophages were infected for 2 h with F. tularensis LVS (F.t.) at an MOI of 500, and at indicated time points, the cytoplasmic portions were analyzed for cytochrome c by immunoblotting. Positive-control cells were treated with 1 μg of staurosporine (Stau) ml−1 for 12 h, and a sample of uninfected cells (Mock) were prepared at 18 h. Relative band intensity was analyzed using a Gel-Pro analyzer (version 3.1; Media Cybernetics L.P., Silver Spring, Md.), and the mock band level was set at 1.0. (B) Mitochondrial membrane potential was disturbed in infected macrophage cells. Eighteen hours after infection, cells were collected and stained with Mitosensor dye to measure mitochondrial membrane potential. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis showed that only 10% of infected cells exhibited intense red fluorescence compared to uninfected cells (46%). FL3-H, red fluorescence intensity; M1, quantification marker of strongly fluorescent cells.