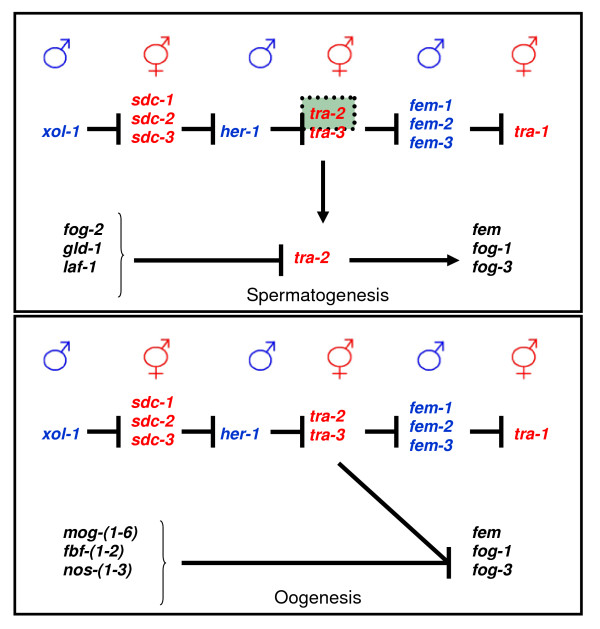
Figure 10.
Gene interactions that allow spermatogenesis and oogenesis in the hermaphrodite C.elegans, as opposed to the gene pathway in the soma. The top half of each frame displays the gene pathway for sex determination in the C.elegans soma and the bottom half the changes that concern the hermaphrodite germline. During the fourth larval stage (L4), a special set of genes expressed in the germline (fog-2, gld-1, laf-1) allows spermatogenesis to occur in hermaphrodites by interfering with the original sex determination pathway (inhibition of tra-2 that leads to the activation of the fem gene products and others such as fog-1 and fog-3). Once spermatogenesis is over and the hermaphrodite enters its mature stage (M), the original sex determination pathway is re-established (tra-2 becomes active again) in the germline of adult hermaphrodites and makes the switch to oogenesis (by inactivating the genes fem, fog-1 and fog-3 gene products that allowed spermatogenesis).