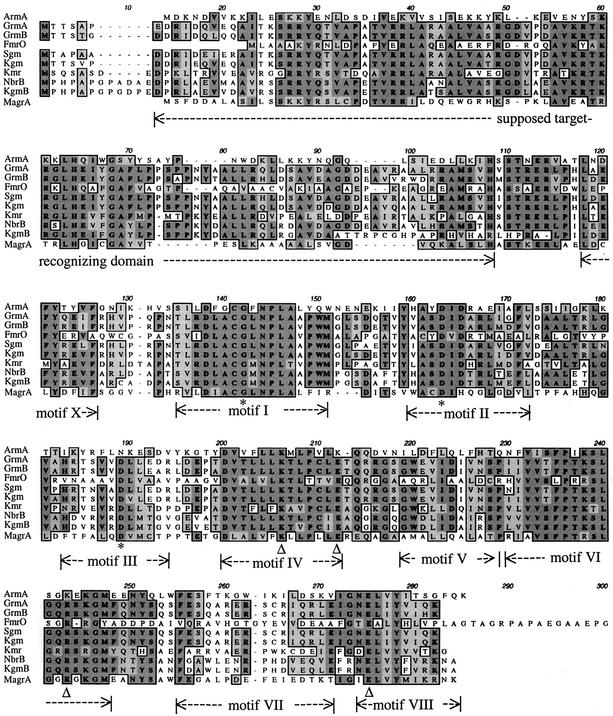
FIG. 1.
Alignment of the deduced sequences of the Agr family. Identical amino acids in all proteins are highlighted with a dark grey background. Homologous amino acids are highlighted with a light grey background. Sequences are from K. pneumoniae (ArmA), M. purpurea (GrmA; GenBank accession number P24618), M. rosea (GrmB; GenBank accession number P24619), M. olivasterospora (FmrO; GenBank accession number Q08325), M. zionensis (Sgm; GenBank accession number A45282), S. lividans (Kgm; GenBank accession number CAC93944), S. kanamyceticus (Kmr; GenBank accession number CAA75800), S. hindustanus (NbrB; GenBank accession number AAB95477), S. tenebrarius (KgmB; GenBank accession number S17717), and P. aeruginosa (MagrA; GenBank accession number AB083212). Due to spatial constraints, the C-terminal extension of FmrO (ATRPVVDVPATARPDADRVDPTG) was omitted. Conserved residues postulated to form the active site in both m7G methyltransferase families are indicated with open triangles. Conserved residues predicted to form the common AdoMet-binding site are indicated with asterisks, and common motifs are delineated by double-head dashed arrows.