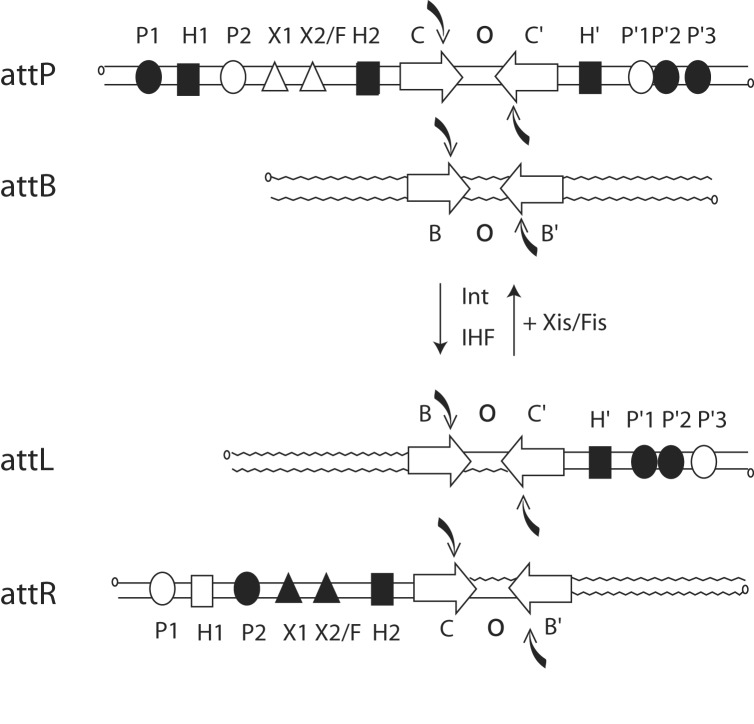
Fig. 1.
Location and occupancy of protein-binding sites during integrative and excisive recombination. Integrative recombination between the phage attP and bacterial attB sites requires the phage-encoded Int protein and the host-encoded IHF to generate the attL(Left) and attR(Right) prophage sites. Excisive recombination between attL and attR additionally requires the phage-encoded Xis protein and is assisted by the host-encoded Fis protein. Protein-binding sites in the arms of attP, attL, and attR that are occupied during integration and excision are shown as filled symbols. Int has four core-type sites (C, C′, B, and B′) that flank the 7-bp overlap region (O) as inverted repeats (inverted open arrows) and encompass each of the DNA-cleavage sites (curved filled arrows). There are five arm-type Int-binding sites (circles): two single sites in the P arm (P1 and P2) and three adjacent sites in the P′ arm (P′1, P′2, and P′3). IHF has three binding sites, H1, H2, and H′ (squares), and Xis has two binding sites, X1 and X2 (triangles), one of which (X2) overlaps with the single Fis-binding site (F).