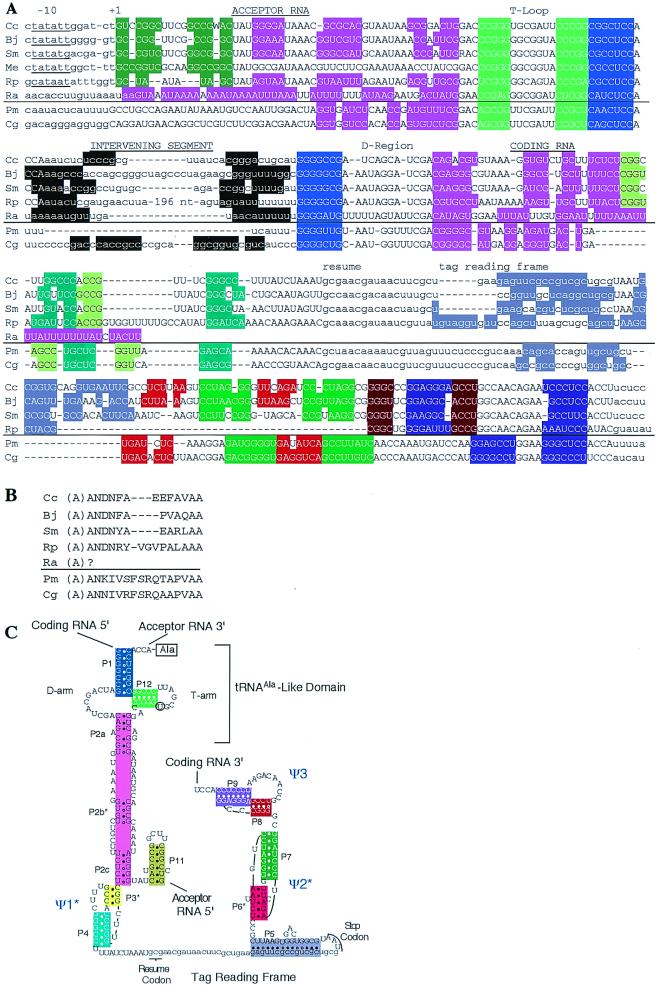
Figure 4.
Permuted tmRNA genes. (A) Alignment. Sequences from the α-proteobacterial lineage (including the mitochondrial sequence, Ra) are shown above the line in each section; those from the cyanobacterial lineage are shown below the line. Color coding marks potential base pairing; note that some marked pairings are not confirmed by base pair covariation. Lowercase is used to represent 5′ and 3′ segments that are predicted to be absent in mature tmRNAs, intervening segments, and tag reading frames. Likely −10 promoter sequences are underlined. Intrastrain sequence variation (ambiguously called bases) is suggested by conflict in equally reliable sequence data for C. crescentus and S. meliloti. Abbreviations for sequence data: Cc, C. crescentus; Bj, Bradyrhizobium japonicum; Sm, S. meliloti; Me, M. extorquens; Rp, R. prowazekii; Ra, Reclinomonas americana mitochondrion; Pm, P. marinus; Cg, C. gracile PCC 6307. An enhanced version of this alignment is displayed at www.indiana.edu/∼tmrna. (B) Encoded peptide tags. Because no tag-like sequence is found in Reclinomonas, it is unclear whether it donates its charging alanine (in parenthesis). (C) Predicted secondary structure of Caulobacter tmRNA. Pairings are numbered by possible analogy with standard tmRNA; those not supported by base pair covariation are marked with asterisks, as are the corresponding pseudoknots (Ψ) that would contain them. The U, which may be modified to T in the T arm, is circled.