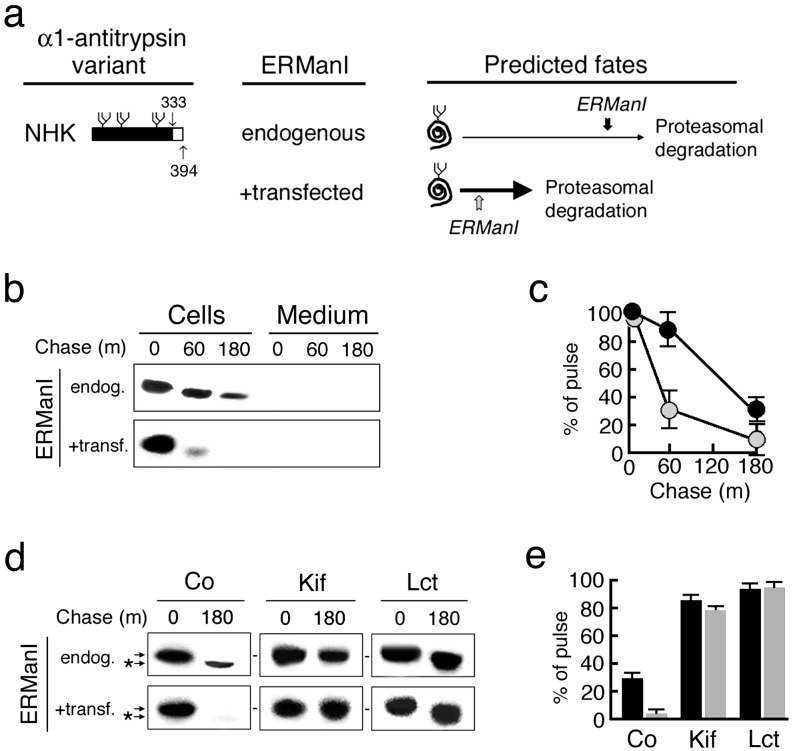
Fig. 2.
The consequences of elevated ER mannosidase expression on the intracellular stability of human AAT variant null(Hong Kong) after biosynthesis. (a) Depicted are the C-terminal truncation and the predicted fates of newly synthesized variant null(Hong Kong) (NHK) in response to the basal (endogenous) and overexpressed (+transfected) ERManI concentrations in Hepa1a. The placement of vertical arrows depicts the predicted relative timing of the glycan modification under both conditions. (b) Pulse–chase radiolabeling and fluorographic detection of immunoprecipitated null(Hong Kong) (NHK) from cells and medium. (c) Quantitation of the results shown in b under endogenous (black circles) and elevated (shaded circles) ERManI concentrations. (d) Shown are the effects of kifunensine (Kif) and lactacystin (Lct) on the fate of newly synthesized null(Hong Kong), and on the discrete mobility shift (*) in SDS/PAGE. (e) Shown is quantitation of pulse-radiolabeled null(Hong Kong) in response to the endogenous (black bars) and elevated (shaded bars) concentrations of ERManI, and in response to specific treatments.