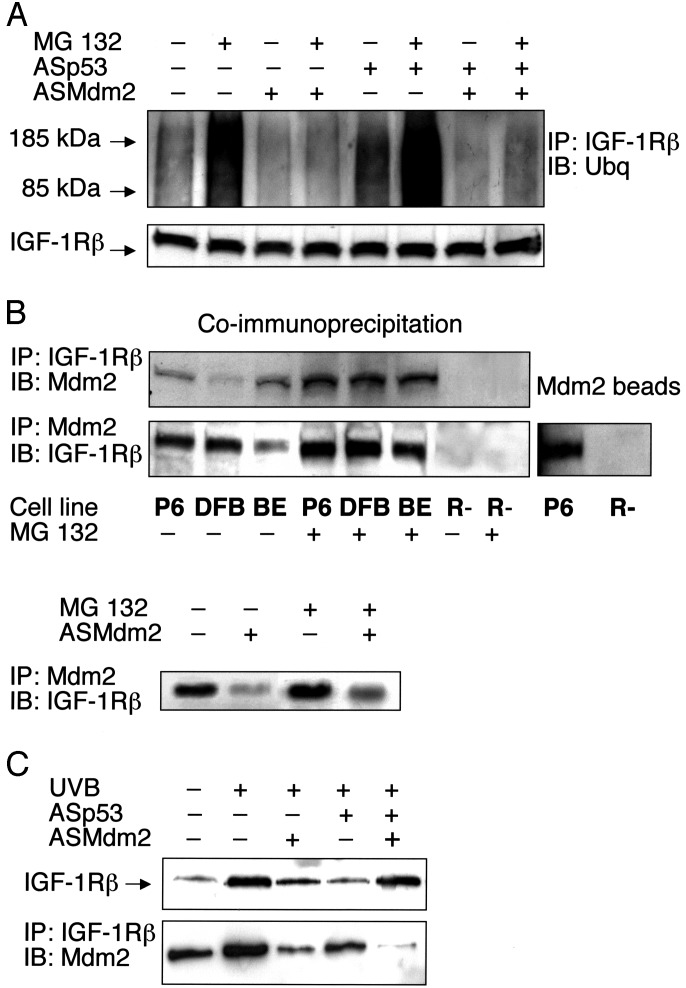
Fig. 4.
Ubiquitination of IGF-1R and association with Mdm2. (A) DFB cells either remained untreated or were treated with ASp53, ASMdm2, or both as indicated for 12 h, after which the proteasome inhibitor MG 132 (50 μM) was added, or not, for an additional 6 h. IGF-1R was immunoprecipitated by a
β-subunit antibody. Equal amounts of purified IGF-1R immunoprecipitates (to compensate for decrease in ASp53-treated cells), verified in the lower panel, were resolved by SDS/PAGE and finally detected by Western blotting using an antibody to ubiquitin. (B Upper) Total proteins isolated from the indicated cell lines were immunoprecipitated with an IGF-1R β-subunit antibody and immunoblotted by an Mdm2 antibody, or vice versa. (B Lower Left) BE cells were pretreated with ASMdm2 for 12 h, and the proteasome inhibitor MG 132 was added, or not, for an additional 6 h before coimmunoprecipitation. (B Right) Total protein lysates from P6 and R- cells were mixed with Sepharose beads of recombinant Mdm2 (see Materials and Methods). The Mdm2 beads were analyzed by Western blotting using an IGF-1R β-subunit antibody. (C Upper) UV-irradiated human melanocytes were treated as indicated for 6 h. Thereafter, analysis of IGF-1R was performed as described for the experiments on the melanoma cell lines. (C Lower) UV-irradiated melanocytes were treated as indicated for 6 h. Immunoprecipitation using an IGF-1R β-subunit antibody and immunoblotting with an Mdm2 antibody was then done. The experiments were repeated two to four times with similar results.