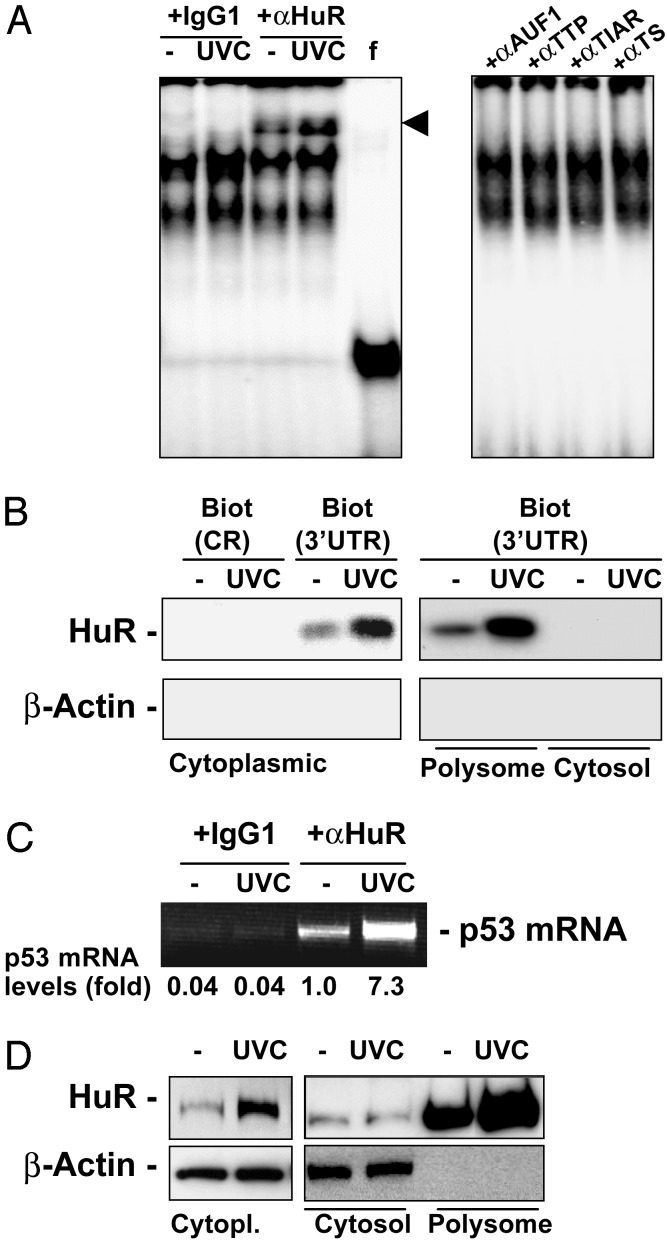
Fig. 4.
HuR binds to the p53 3′ UTR in a UVC-dependent manner. (A) REMSA supershift using either IgG1 or an anti-HuR antibody (11) (Left), or antibodies recognizing the RNA-binding proteins shown (Right). f, free probe, digested with RNase T1 but left without incubating with cytoplasmic lysates; arrowhead, supershift of HuR-containing complexes. (B) Detection of HuR after pull-down by using biotinylated p53 transcripts CR and 3′ UTR (described in Fig. 3 Upper). After incubations with proteins present in cytoplasmic, cytosolic, or polysomal fractions of cells that were either left untreated or treated with 15 J/m2 UVC, the presence of HuR and β-actin was detected by Western blotting. (C) IP by using either anti-HuR antibody or IgG1 under conditions that preserve the association of RNA-binding proteins with target mRNAs was followed by RT-PCR analysis to detect endogenous p53 mRNA; PCR products were resolved by electrophoresis in 1.5% agarose gels stained with ethidium bromide. (D) Subcellular localization of HuR in cytoplasmic (Cytopl.), cytosolic (Cytosol), and polysomal (Polysome) fractions prepared from cells that were either left untreated or UVC-treated.