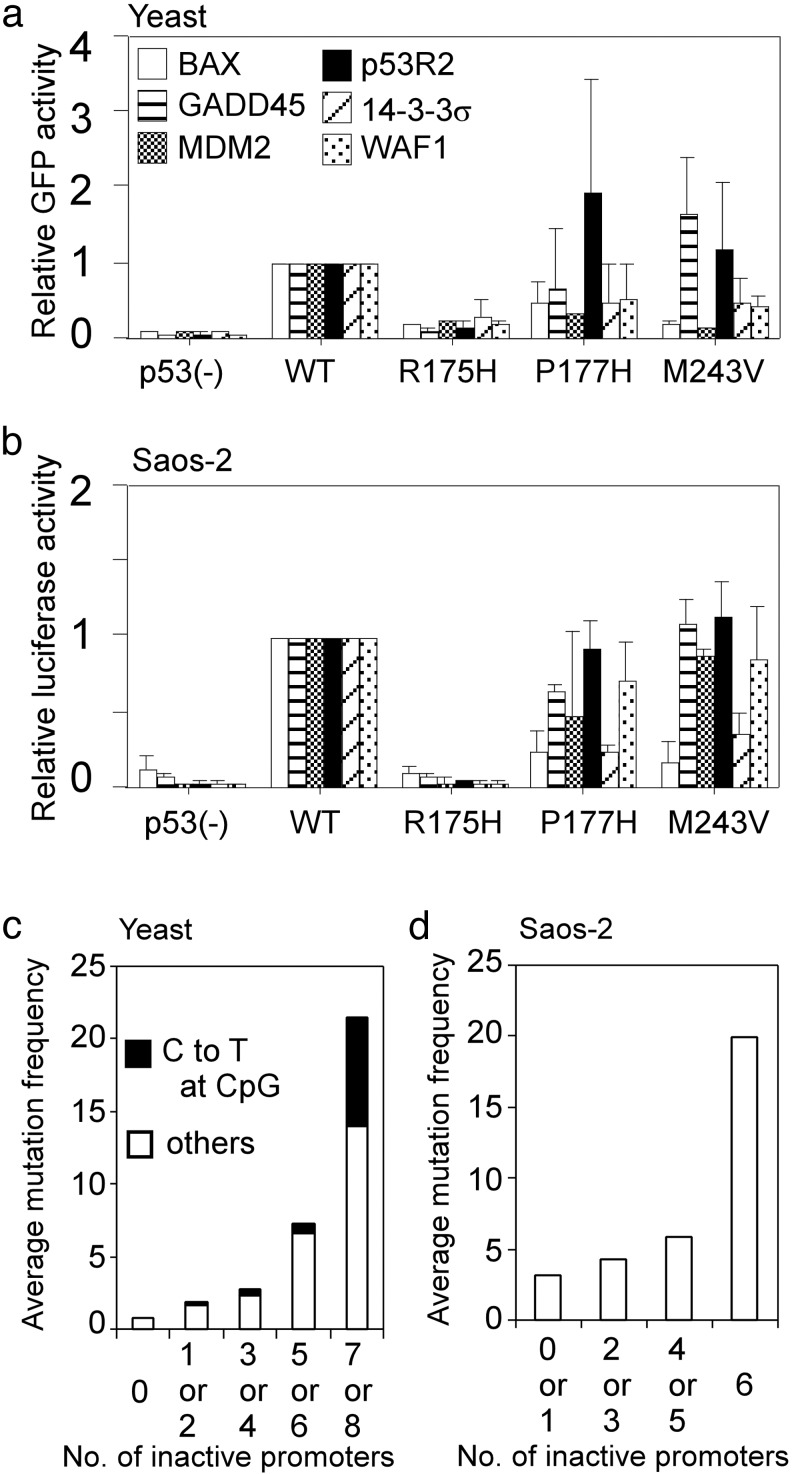
Fig. 4.
Comparison of p53 transactivation function in yeast with that in human cells. (a) Transactivities of three representative p53 mutants (R175H, P177H, and M243V) through the indicated six p53-binding sequences were shown as relative GFP (EGFP or Ds-Red) intensities against wild-type (WT) p53 activities. (b) The three mutants, which were the same as a were examined for their abilities to transactivate the luciferase reporter gene through the six corresponding promoters in Saos-2 cells. Bar, SD. (c) Average mutation frequency on number of inactivated promoters. Based on the yeast experiment, the 2,314 mutants were fractionated on the number of inactivated promoters for eight distinct p53-binding sequences. (d) Average mutation frequency on number of inactivated promoters based on the transactivities of 89 selected mutants in Saos-2 cells. Note that we did not choose mutants that theoretically occur by C-to-T transition at CpG sites as well as the top 10 hot spot mutants to avoid strong bias. In both c and d, mutation frequency for each mutant was derived from the IARC database and was averaged in each fraction.