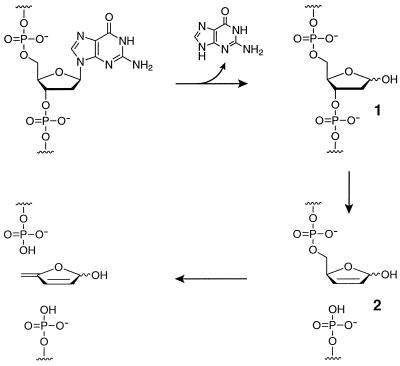
Figure 1.
DNA strand scission resulting from depurination and subsequent β-elimination at the AP site. Hydrolysis at the C1′ position of deoxyguanosine results in release of guanine and formation of an AP site (1). The α- and β-hemiacetals are in equilibrium with the open chain aldehyde, which is susceptible to β-elimination that results in cleavage of the adjacent 3′ phosphoester (2). This product in turn undergoes cleavage of the 5′ phosphoester under alkaline conditions.