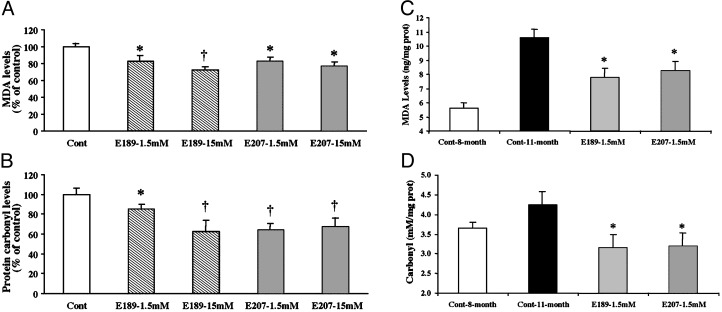
Fig. 3.
Effects of chronic treatment with EUK-189 or EUK-207 on lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation in brain homogenates. At the end of the behavioral experiments, the mice were killed and their brains (minus cerebellum) were frozen. Levels of lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation (protein carbonyls) were determined as described in Materials and Methods. Results were expressed as percentage of vehicle control value (mean ± SEM, n = 12; A and B). *, P < 0.05; †, P < 0.01 (Student's t test). Levels of lipid peroxidation and protein carbonyls were also determined in brain homogenates from the 8-month-old control C57 mice. The levels of lipid peroxidation were expressed as nmol malondialdehyde equivalent per mg of protein (C) and the levels of protein oxidation as nmol carbonyl per mg of soluble extracted protein (D), and are means ± SEM of 12 mice [C: *, P < 0.05 as compared with either 8- or 11 month-old control mice; D: *, results not significantly different from 8-month-old control mice; †, P < 0.005 as compared with 11-month-old vehicle mice (Student's t test)].