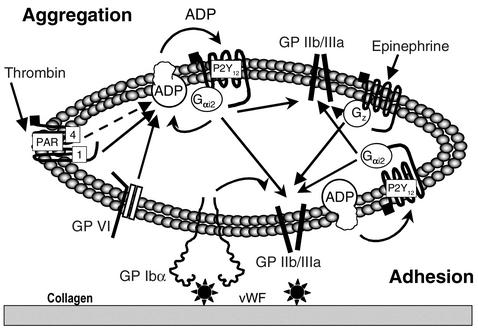
Figure 9.
P2Y12 at the crossroads of the arterial thrombotic process. Upon vascular injury, various thrombogenic components (i.e., collagen/vWF) are exposed to arterial blood flow. Platelet membrane GP Ibα recognizes the activated conformation of vWF, inducing various signals inside the platelets, and leads to GP IIb-IIIa activation. ADP released from platelet-dense granules participates in the firm adhesion/activation step by interaction with P2Y12, leading to activation of GP IIb-IIIa. Simultaneously, collagen-induced platelet activation through GP VI (42) leads to GP IIb-IIIa activation, resulting in adhesion and aggregation. ADP-P2Y12 interactions (downstream of GP Ibα signaling and subsequent stimulation of the thrombin receptor) (43) also mediate the recruitment of circulating platelets to a growing thrombus. P2Y12 might also affect thrombus stability as a result of low surface expression of known secondary platelet agonists (P-selectin, Gas6, CD40L [see ref. 44] not shown on the scheme). PAR, protease-activated receptor.