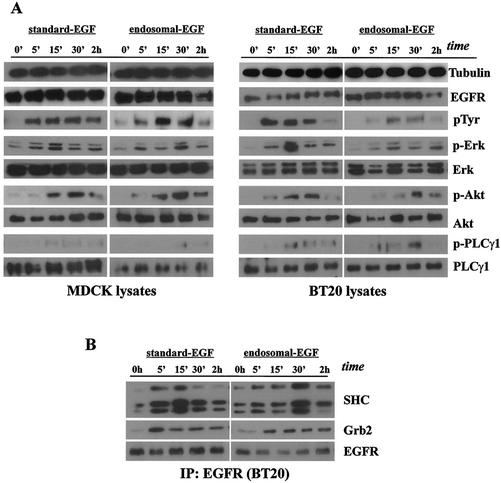
FIG. 6.
Stimulation of EGFR and various signal transduction pathways by the first pulse of standard and endosomal EGFR signaling. Subconfluent cultures of MDCK and BT20 cells were serum starved for 48 h and treated for 1 h with EGF (100 ng/ml) to assay receptor activation and signal transduction originating at the plasma membrane (surface EGF) or incubated with AG1478 and EGF, acid stripped of recycled ligand, and washed free of AG1478 to assay receptor activation and signal transduction originating at the endosome (endosomal EGF). (A) Initial activation of EGFR and downstream signaling effectors following surface and endosome EGF treatment. Cell lysates, collected at the times indicated, were subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies to EGFR, phosphotyrosine 1186 of EGFR (p1186), phospho-Erk1/2, Erk1/2, phospho-Akt, Akt, phospho-PLC-γ1, and PLC-γ1. Tubulin antibody was used to assess protein loading. For the endosome EGF pulse, samples collected at 0 h preceded the acid strip step, although they had already been preincubated with AG1478 and EGF. (B) Ligand-induced association of EGFR with SHC and Grb2 following surface and endosome EGF treatment. BT20 lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with mouse anti-EGFR antibody and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies to Grb2, SHC, and EGFR.