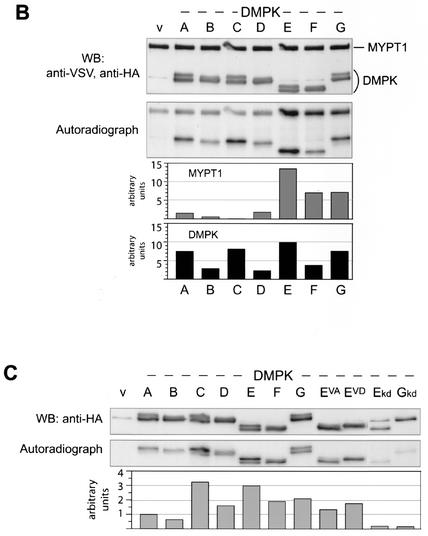
FIG. 4.
Differential kinase activity and (auto)phosphorylation of DMPK isoforms and mutants. (A) HA-DMPK isoforms A to G, EVA and EVD were expressed in COS-1 cells. Cell extracts were prepared and tested for HA-DMPK by Western blotting (upper panel). Extracts were used in a kinase assay with substrates KKRNRRLSVA (peptide 2) or KKLRRTLSVA (peptide 17) (middle panel). All DMPK isoforms and mutants showed comparable activities towards these peptides. Immunoprecipitated DMPK (after performing assay with peptide 2) was blotted to PVDF membrane to control input (Coomassie brilliant blue [CBB]staining) and examine DMPK autophosphorylation. All isoforms were autophosphorylated (i.e., upper bands in VSGGG-containing isoforms), but isoforms lacking VSGGG showed lower autophosphorylation activity. (B) HA-DMPK isoforms A to G were used in a kinase assay with full-length MYPT1 protein as substrate. Input of MYPT1 and DMPK was verified by Western blotting (upper panel; note aspecific anti-HA band, unrelated to DMPK, in vector-only lane [lane v]). Phosphorylation of MYPT1 and autophosphorylation of DMPK became evident by autoradiography, which was quantified by phosphorimager analysis (lower two panels; values in arbitrary units, after background [lane v] subtraction). (C) COS-1 cells expressing HA-DMPK isoforms and mutants were cultured in the presence of [32P]orthophosphate to examine in vivo phosphorylation of DMPK. DMPK was immunoprecipitated, separated by SDS-PAGE, and blotted to PVDF membrane. The blot was used for autoradiography (middle panel) and phosphorimager analysis (lower panel). Values are presented in arbitrary units, after background (vector-only lane [lane v]) subtraction. Note that kd mutants E and G were less well expressed (upper panel), which partly explains their low signals on autoradiography.