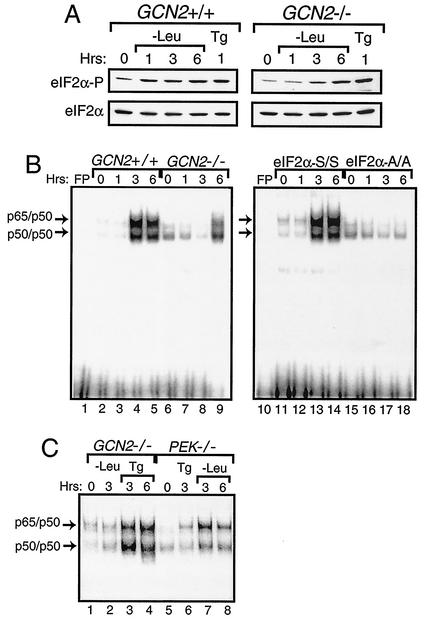
FIG. 3.
Activation of NF-κB during amino acid conditions requires phosphorylation of eIF2α by GCN2 protein kinase. (A) GCN2+/+ and GCN2−/− MEF cells were deprived of leucine for between 1 and 6 h and subjected to thapsigargin for 1 h or to no stress (0 h) as indicated. Phosphorylation of eIF2α was assayed for by immunoblot analysis using antibody specific to eIF2α phosphorylated at Ser-51 (eIF2α∼P), and total eIF2α levels (eIF2α) were measured using antibody that recognizes both phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated versions of eIF2α. (B) Nuclear lysates were prepared from GCN2+/+ (lanes 2 to 5), GCN2−/− (lanes 6 to 9), S/S (lanes 11 to 14), and A/A (lanes 15 to 18) MEF cells deprived of leucine for the indicated number of hours and were assayed for binding with radiolabeled DNA containing a NF-κB binding site by the EMSA. (C) NF-κB binding was measured by the EMSA using nuclear lysates prepared from GCN2−/− and PEK−/− MEF cells that were starved for leucine or exposed to thapsigargin for the indicated number of hours. Arrows indicate DNA complexed with p65/p50 or p50/p50. Free probe (FP) indicates that only the radiolabeled NF-κB DNA was used in the assay, and the radiolabeled DNA at the bottom of panel B is unbound probe.