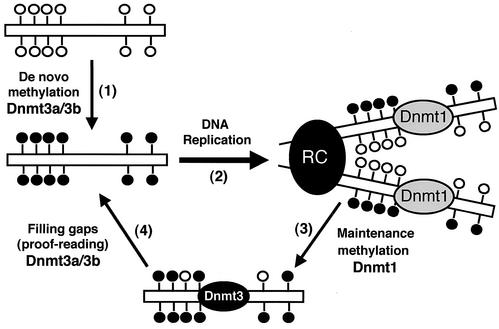
FIG. 8.
Model for the distinct roles of Dnmt1 and Dnmt3a/3b in de novo and maintenance methylation. (Step 1) Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b establish new DNA methylation patterns by de novo methylation of symmetric CpG dinucleotides (lollipops). (Step 2) Upon DNA replication, the new synthesized DNA becomes hemimethylated at CpG sites. (Step 3) Dnmt1, which is localized to the replication complex (RC), restores full methylation by methylating hemimethylated DNA. However, some CpG sites are left untouched by Dnmt1 and remain hemimethylated. (Step 4) Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b, which may also localize to the RC, recognize unmethylated CpG sites and restore methylation via de novo methylation. In summary, Dnmt1 is the major maintenance methyltransferase, and it has little or no de novo methylation activity in vivo. Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b possess active de novo methyltransferase activity in vivo and are essential for the establishment and maintenance of DNA methylation patterns.