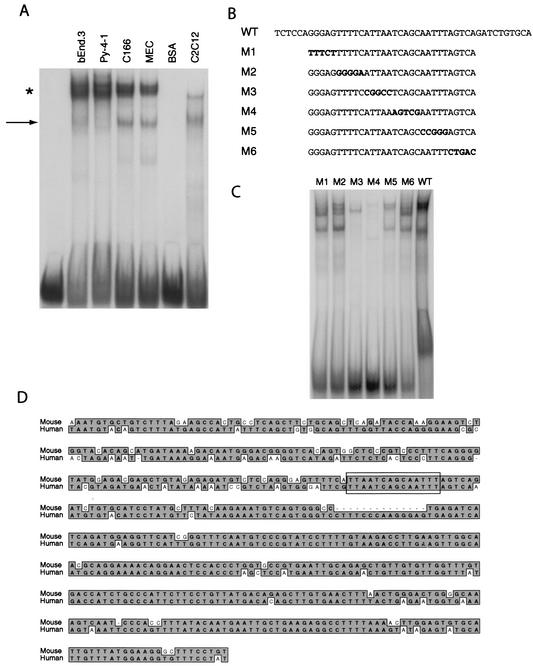
FIG. 2.
Identification of the minimal DNA sequences in the flk1 intronic enhancer necessary for nuclear protein interactions. (A) Nuclear protein interactions with the flk1 cis-acting element detected by EMSA. The probe corresponding to bp 150 to 195 of the mouse flk1 first-intronic enhancer was used to characterize nuclear protein interactions with endothelial and nonendothelial nuclear extracts. The arrow denotes a rapidly migrating complex, while the asterisk denotes a more intense, slowly migrating complex. (B) Mutant oligonucleotides used in EMSA. Residues that differ from the wild-type sequence are in boldface. (C) EMSA with C166 nuclear extract with mutant probes described in panel B. (D) Comparison of partial sequences of the mouse and human flk1 first introns. Identical residues are highlighted, and the nuclear protein-binding site identified by DNase I footprinting and EMSA is boxed.