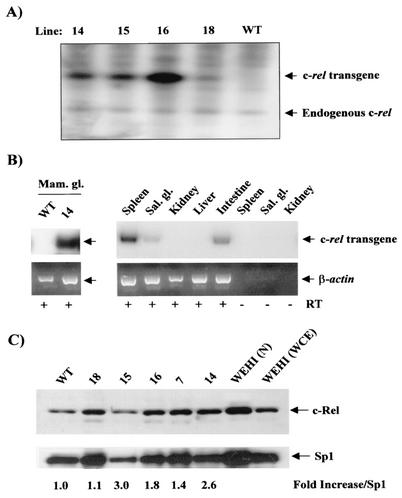
FIG. 1.
MMTV-LTR-driven c-rel transgene expression in FVB/N mice. (A) Identification of founder lines. Genomic tail DNA was prepared from the indicated potential founders MMTV-c-rel transgenic mice, and samples (10 μg) digested with PstI and subjected to Southern blot analysis for c-rel using the 2.2-kb fragment, encompassing the MMTV-LTR promoter and an ∼1-kb fragment of mouse c-rel cDNA, released from the MMTV-c-rel plasmid digested with PstI, as a probe. The positions of the bands derived from the c-rel transgene and the endogenous c-rel gene are as indicated. (B) Transgenic c-rel expression. Total RNA was isolated from the indicated organs of WT FVB/N or line14 MMTV-c-rel mice at day 18.5 of the first pregnancy, and subjected to DNase treatment. Samples (5 μg) were subjected to RT-PCR analysis, in the presence (+) or absence (−) of RT to control for DNA contamination, using c-rel transgene-specific oligonucleotides, amplifying a 236-bp fragment. Similar analysis of β-actin RNA levels confirmed the integrity of the reverse transcription reaction. (C) Total c-Rel expression. Mammary glands were removed from WT FVB/N or the indicated transgenic line mice at day 18.5 of the first pregnancy. Nuclear extract were prepared, and samples (20 μg) subjected to immunoblot analysis of c-Rel, and Sp1, as control for loading. As additional controls, nuclear extracts and WCEs from the WEHI 231 immature B-lymphoma cells, which express high constitutive levels of c-Rel (40), were similarly analyzed. The values of c-Rel normalized to Sp1 level relative to the WT sample are displayed below.