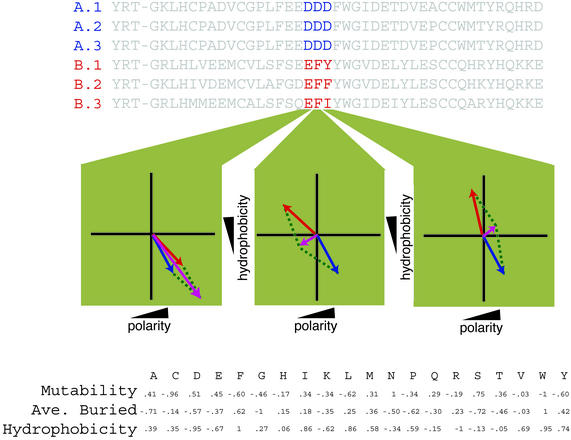
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of chemical-property vectors. Vectors are constructed for each MSA position independently for a given subfamily and again for the entire family. Here, an example MSA containing six sequences from two subfamilies is plotted in two dimensions (hydrophobicity on the y and polarity on the x axis). Red and blue vectors represent subfamily vectors for subfamilies A and B, respectively. In the leftmost plot, they represent the sums of three Ds for subfamily A, or three Es for subfamily B. A purple vector represents the overall vector at the MSA position. The subfamily's FamVal scores are computed by comparing the distances (green dotted lines) between the subfamily-vector endpoints and the overall-vector endpoints, weighted by multiplying by sin (θ/2). A table containing normalized chemical-property scales used for FamVal scores in this study is shown at the bottom.