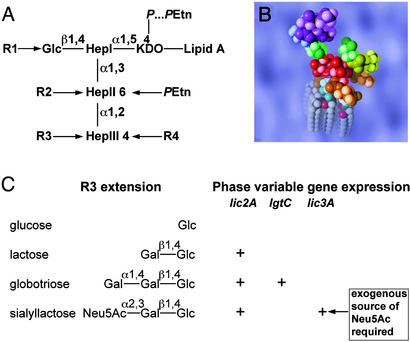
Fig. 3.
Hi LPS comprises a heterogeneous mixture of glycoforms consisting of an oligosaccharide moiety attached to a membrane anchoring lipid A component. (A) Structural model of the conserved inner core region of the oligosaccharide portion of the molecule. (B) Space-filling molecular model of the minimum energy conformer of the sialyllactose containing LPS glycoform of NTHi strain 375 calculated by a Monte Carlo method (22). The conserved l-glycero-d-manno-heptopyranosyl trisaccharide (HepI–HepIII), depicted in red, is linked to the lipid A portion of the molecule (turquoise and gray) via a phosphorylated KDO residue (brown). The triheptosyl inner-core unit is substituted by a β-d-glucopyranose residue (Glc; green) at the O-4 position of HepI and by a phosphoethanolamine residue (PEtn; brown) at the O-6 position of HepII. In NTHi 375, 285, and 162 LPS, the Glc residue is substituted at O-6 by a phosphocholine residue (R1 = PCho; yellow). In NTHi strain 486 (R1 = H), HepII is substituted at the O-3 position by an α-d-glucopyranose which, in turn, is substituted by PCho at the O-6 position (R2 = PCho-6Glc). NTHi strain 375 can also carry a PEtn group on HepIII (R4 = H or PEtn). As shown in C, the NTHi strains used in this study can exhibit oligosaccharide chain extension from HepIII (R3) through sequential addition of sugar units (6, 7). LPS glycoforms containing β-d-glucopyranose, lactose, globotriose, and sialyllactose oligosaccharide chains have been identified (6, 7, 17, 23). The relative proportions of these glycoforms in the LPS from a particular strain depend on the expression of phase variable genes lic2A, lgtC, and lic3A (7, 24).