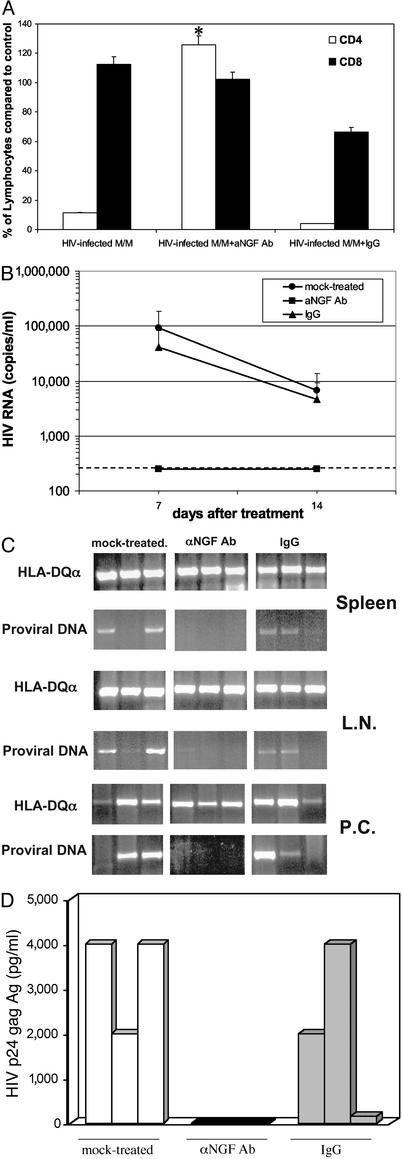
Fig. 4.
NGF starvation prevents HIV infection in hu-PBL-SCID mice challenged with infected macrophages. (A) Percentage of CD4+ T lymphocytes (white bars) and CD8+ T lymphocytes (black bars) were measured in hu-PBL-SCID mice at day 14 after challenge with HIV-infected macrophages and treatment with anti-NGF mAb (HIV-infected M/M+aNGF Ab). A group of mice was treated with an isotypic Ab (HIV-infected M/M+IgG); *, P < 0.05 compared with CD4 in infected but untreated hu-PBL-SCID mice. (B) HIV-1 RNA was measured in hu-PBL-SCID plasma at days 7 and 14 after HIV macrophage challenge and treatment with either anti-NGF Ab (▪) or an isotypic IgG Ab (▴), or no treatment (•); P < 0.05. The dashed line defines the threshold of HIV-RNA detection. (C) Mice were killed 2 weeks after infection, then the spleen, lymph nodes (L.N.), and peritoneal cells (P.C.) were analyzed for the presence of HIV-1 proviral copies and HLA-DQ expression by DNA PCR. (D) HIV-1 p24 antigen was measured by ELISA in supernatants of peritoneal cells isolated from hu-PBL-SCID mice challenged with HIV-infected M/M treated with aNGF Ab (black bars) or an IgG isotypic Ab (gray bars), or mock-treated (white bars). In this experiment, three mice for each group were used. Each bar corresponds to a single mouse.