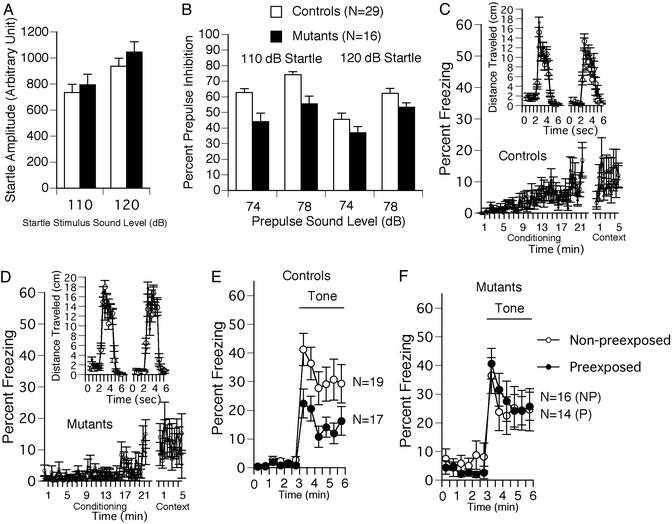
Fig. 3.
Impaired prepulse inhibition (A and B) and latent inhibition (C–F) of CN mutant mice. Startle amplitude was not different between genotypes (A), but the percentage prepulse inhibition was significantly smaller in CN mutants compared with controls (B). Percent freezing during the conditioning phase was significantly less in CN mutants (D) compared with controls (C), most likely due to their hyperactivity. CN mutants traveled longer distances in response to shocks than controls (Insets in D and C, respectively). Freezing during contextual testing was not significantly different between genotypes (C and D). In cued testing, the percent freezing for the P group was significantly lower than that of the NP group in control mice, indicating significant latent inhibition in control mice (E). In contrast, the CN mutants failed to show a significant latent inhibition (F).