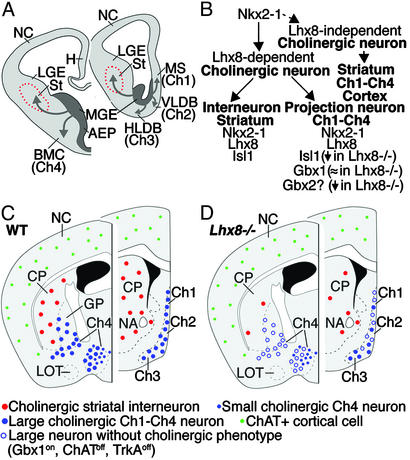
Fig. 6.
Schemas illustrating the origin and migration of cholinergic neurons derived from the basal telencephalon and the genes that are involved in their specification and differentiation. (A) The schematic of transversal hemisections through the embryonic telencephalon summarizes the expression of Lhx8. Lhx8+ neurons differentiate as interneurons in the striatum or as projection neurons in the basal telencephalon (Ch1–Ch4 cholinergic groups). (B) Model describing some of the genes that regulate production of cholinergic neurons in the telencephalon. Nkx2-1 regulates production of cells that express Lhx8 (11), which is necessary for the differentiation of most cholinergic neurons in the basal telencephalon (this study). Nkx2-1 is also required for the specification of GABAergic neurons (11), and some cholinergic neurons in the telencephalon develop in the absence of Lhx8 function (dashed line). In the striatum, cholinergic interneurons express Nkx2-1, Lhx8, and Isl1. In addition to Nkx2-1 and Lhx8, cholinergic projection neurons in the basal telencephalon express Isl1 and Gbx1. Whereas the Gbx1 expression is maintained, the Isl1 expression is reduced in Lhx8 mutants. The expression of Gbx2 is also reduced in the mantle zone of the MGE in Lhx8 mutants. Although Gbx2 is not expressed in the mature cholinergic neurons (17), its expression in the MGE suggests that it may be expressed in the progenitors of the cholinergic neurons. (C and D) Schemas illustrating the distribution of ChAT+ cells in the adult telencephalon of control and Lhx8 mutant mice. Lhx8 mutation preferentially blocks the differentiation of cholinergic interneurons in the striatum and large projection neurons in the basal forebrain. In Lhx8 mutants, small ChAT+ cells are still present in the cortex and basal forebrain. Expression of Gbx1 in the basal forebrain of Lhx8 mutants suggests that cholinergic cells are born in Lhx8 mutants, but they fail to differentiate properly (i.e., lack ChAT and TrkA expression). AEP, anterior entopeduncular region; BMC, basal magnocellular complex; Ch1–Ch4, Ch1–Ch4 cholinergic cell groups; CP, caudateputamen; GP, globus pallidus; H, hippocampus; HLDB, horizontal limb of diagonal band; LGE, lateral ganglionic eminence; LOT, lateral olfactory tract; MGE, medial ganglionic eminence; MS, medial septal nucleus; NA, nucleus accumbens; NC, neocortex; St, striatum; VLDB, vertical limb of diagonal band.