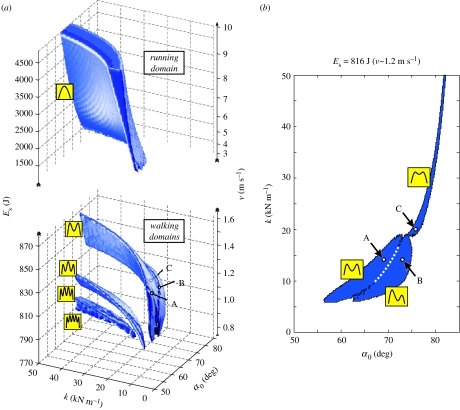
Figure 4.
Parameter domains for stable walking and running. (a) Combinations of angle of attack α0, spring stiffness k and system energy Es leading to stable locomotion are shown. Related to Es, the locomotion speed v is shown, which is the average speed of all solutions that belong to one system energy (maximum deviation 0.1 m s−1 at Es=800 J). The model finds stable walking at low energies or slow speeds (walking domains): next to the domain with double-peak patterns of the vertical GRF, domains with multi-peak patterns exist (small icons). Owing to the limited scan resolution, only domains with up to five peaks are resolved, and the four- and five-peak domains seem to overlap. Circles indicate the parameter sets of the examples A–C shown in figure 3. In addition to walking, the model finds stable running with single-peak vertical GRF above an energy or speed gap of about 500 J or 1.5 m s−1 (running domain). Note the different scales of system energy at the walking domains and the running domain. (b) A slice at Es=816 J (v∼1.2 m s−1) through the walking domain with double-peak patterns is shown. Three sub-domains of parameters exist that lead to three qualitatively different steady-state patterns (small icons) exemplified by the three solutions A–C (compare figure 3).