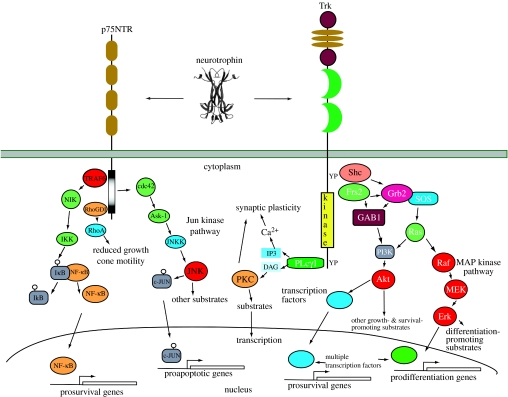
Figure 2.
Neurotrophin signalling. This depicts the interactions of each neurotrophin with Trk and p75NTR receptors and major intracellular signalling pathways activated through each receptor. The p75NTR receptor regulates three major signalling pathways. NF-κB activation results in transcription of multiple genes, including several that promote neuronal survival. Activation of the Jun kinase pathway similarly controls activation of several genes, some of which promote neuronal apoptosis. Ligand engagement of p75NTR also regulates the activity of Rho, which controls growth cone motility. Pro-apoptosis actions of p75NTR appear to require the presence of sortilin, which functions as a co-receptor for the neurotrophins. Sortilin is not depicted in this figure, but is described in the text. Each Trk receptor also controls three major signalling pathways. Activation of Ras results in activation of the MAP kinase-signalling cascade, which promotes neuronal differentiation including neurite outgrowth. Activation of PI3 kinase through Ras or Gab1 promotes survival and growth of neurons and other cells. Activation of PLC-γ1 results in activation of Ca2+- and protein kinase C-regulated pathways that promote synaptic plasticity. Each of these signalling pathways also regulates gene transcription. Many additional adaptors for p75NTR and Trk receptors have been identified which are not depicted in this figure for simplicity, but are described in more detail in the text. Interactions between p75NTR and Trk receptors are not depicted in this figure, but are described in the text. p75NTR also appears to function as constituent of other receptor complexes, most notably the Nogo receptor complex. These interactions and signalling pathways are not depicted here.