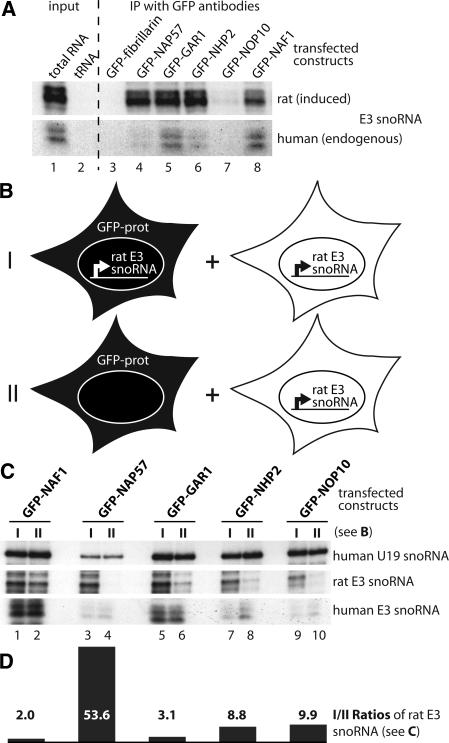
FIGURE 2.
Association of GFP-tagged proteins with H/ACA RNAs in cell lysates. (A) Autoradiograph of induced rat (upper panel) and endogeous human E3 snoRNA (lower panel) detected by RNase A/T1 protection assay in total U2OS cell RNA 24 h after induction of the rat E3 transgene (lane 1) and, as a negative control, in yeast tRNA (lane 2). Lanes 3–8 show the same as lane 1, but the RNA was isolated from immunoprecipitates with GFP antibodies from E3 cell lysates transfected with the indicated GFP constructs and induced for rat E3 expression. One-tenth cell equivalent was used in lane 1 compared to lanes 3–8. (B) Schematic of the two GFP-construct transfection and rat E3 snoRNA induction approaches (I,II) used in C for immunoprecipitation with GFP antibodies followed by snoRNA analysis. Briefly, I was a repetition of the experiment in A, but in II the GFP-tagged constructs were transfected into parent U2OS cells lacking the rat E3 snoRNA transgene. In both cases the transfected cells were mixed with an equal number of untransfected U2OS cells (but induced for transgene expression) and lysed for immunoprecipitation with anti-GFP antibodies. (C) RNase protection analysis of the H/ACA snoRNAs in the immunoprecipitates of the GFP-tagged constructs (indicated on top) following the experimental approach (I, odd lanes) and (II, even lanes) in B. Note that in the cell lysates, only GFP-NAP57 failed to associate with the rat E3 snoRNA expressed in separate cells (lane 4). (D) Graph of the ratios between odd and even lanes from the center panel (rat E3 snoRNA) of C corrected for human E3 snoRNA. The values represent the average from two independent RNase protection assays.