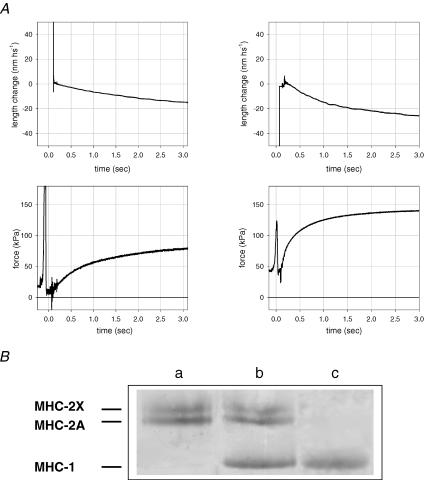
Figure 2. Force development following a T-jump (from 1 to 12°C) in slow (left column) and fast (right column) fibres and identification of fibre types.
A, traces indicate segment length change (upper panel), force response and zero force (lower panel). The artefact before the striation follower signal is due to the fibre travelling in air and within the shadow zone. Slow fibre (type 1 isoform): fibre length, 2.10 mm; segment length under the striation follower, 1.00 mm; average segment sarcomere length, 2.58 μm; CSA, 5200 μm2. Fast fibre (type 2A/2X isoform): fibre length, 2.45 mm; segment length under the striation follower, 0.87 mm; average segment sarcomere length, 2.52 μm; CSA, 9000 μm2. B, MHC isoform identification in single fibres by SDS-PAGE. The areas of migration of MHC-1, MHC-2A and MHC-2X are indicated on the left. Lane a: a single fibre containing MHC-2A and MHC-2X, i.e. a fast, type 2AX, fibre; lane b: a sample from vastus lateralis muscle containing all three adult MHC isoforms; lane c: a single fibre containing MHC-1, i.e. a slow, type 1, fibre.