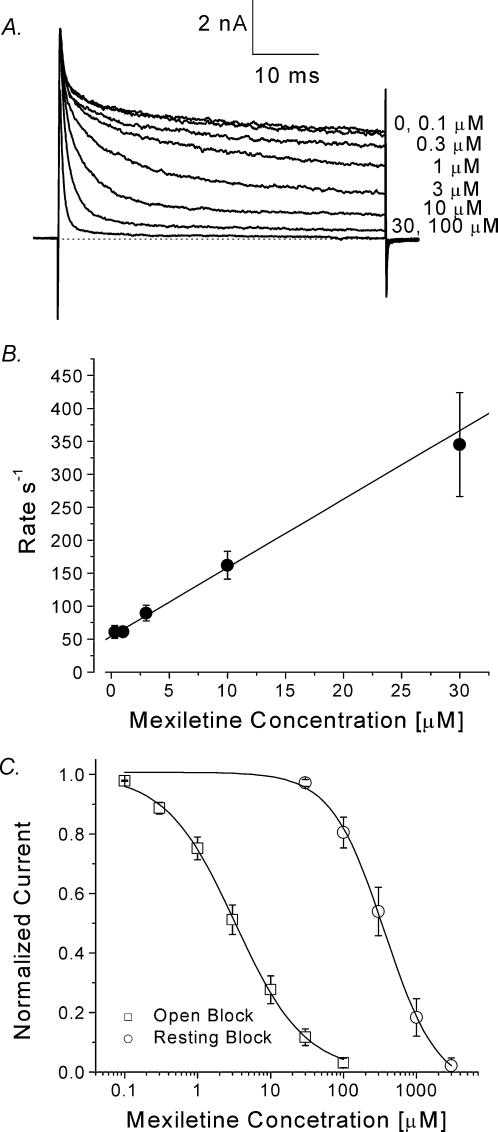
Figure 8. Open-channel block in inactivation-deficient mutant channels by mexiletine.
A, superimposed mutant Na+ currents were recorded at various concentrations of mexiletine. The Na+ currents were evoked by a 50 ms test pulse to +30 mV every 30 s. A steady state at each concentration was established before application of the next concentrated solution. B, the decaying phase of the normalized relative Na+ current was fitted with a single exponential function, and the corresponding τ value (time constant) was inverted and plotted against the corresponding mexiletine concentration (0.3–30 μm). Data were fitted with a linear regression y= 10.4x+ 54.4. The on-rate (kon) corresponded to the slope of the fitted line (10.4 μm−1 s−1) and the off-rate (koff) corresponded to the y-intercept (54.4 s−1). The dissociation constant determined by the equation KD=koff/kon was 5.2 μmC, dose–response curves for open-channel block (relative block at the end of the 50 ms test pulse) and resting-state block (relative block at the peak current) were constructed using the data set as shown in A. All pulses were delivered at 30 s intervals. The amplitudes of Na+ current were measured, normalized to the amplitude of the control, and plotted against the mexiletine concentration. Continuous lines represent fits to the data with the Hill equation. IC50 values ±s.e.m. [Hill coefficients ±s.e.m.] are 3.3 ± 0.1 μm[0.90 ± 0.02] for open-channel block (□, n= 5), and 336.4 ± 20.0 μm[1.2 ± 0.1] for resting-state block (○, n= 5).