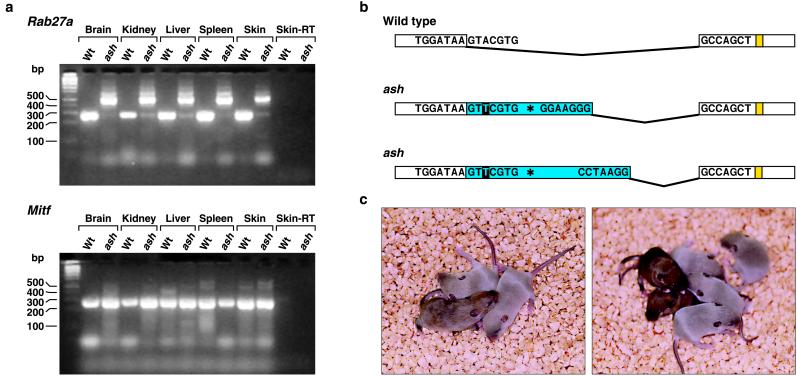
Figure 2.
The ash mutation results from a defect in Rab27a. (a) Reverse transcription–PCR analysis of Rab27a expression in wild-type and homozygous ash mice. Mitf was amplified as a control. Note that ash mice express a mutant Rab27a transcript that is not expressed in wild-type mice. Sequence analysis indicates that this mutant transcript is actually composed of two transcripts, which contain 235 or 252 bp of intron sequence, respectively. Skin-RT, minus reverse transcriptase control. (b) A mutation in the exon 4 splice donor site of Rab27a in ash mice. Exons 4 and 5 are indicated by open rectangles, whereas intron sequences are shown in blue. Exon 5 sequences contributing to the GTP-binding pocket are shown in yellow. The location of the A-to-T transversion in the exon 4 splice donor site (black box) and the stop codon in intron sequence (star) are also indicated. (c) BAC rescue of ash. A partially rescued BAC 514L6 animal is shown on the left, whereas two completely rescued BAC 133L2 animals are shown on the right.