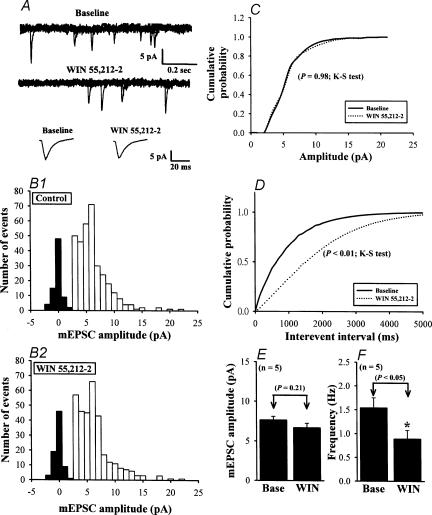
Figure 4. Effect of WIN on the mEPSCs.
A, sample traces of mEPSCs before (Baseline: in the presence of 1 μm TTX to block Na+ channels) and during application of 5 μm WIN. Lower traces are averaged mEPSCs of 35 events each before and after WIN application, demonstrating the lack of effect of WIN on the amplitude and kinetics of mEPSCs. B, amplitude histograms of mEPSCs before (B1) and during WIN application (B2) obtained from 323 and 312 mEPSC events, respectively. C, cumulative probability plots of the mEPSC amplitude before (dotted line) and during (continuous line) application of WIN. No changes occurred in the distribution during WIN application (P= 0.98; Kolmogorov-Smirnov test). D, cumulative interevent interval distribution, illustrating a significant increase in the interevent interval (i.e. decreased frequency; P < 0.01; Kolmogorov-Smirnov test) during WIN application. Data in A–D were obtained from the same neurone. E and F, summary of the effect of 5 μm WIN on the average amplitude (E) and frequency (F) of mEPSCs (n= 5). Data are presented as means ±s.e.m. Asterisk indicates P < 0.05 compared with control (Base). Holding potential was −70 mV.