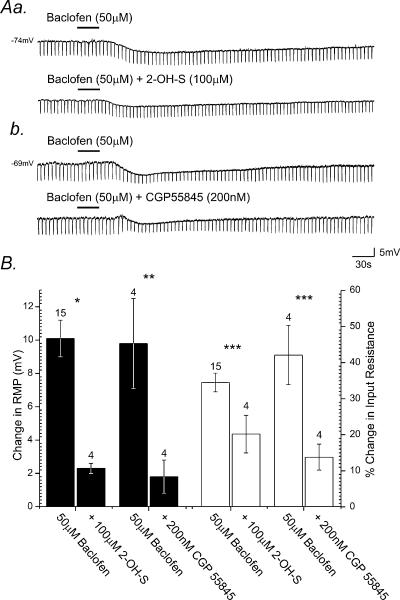
Figure 5. SPNs express postsynaptic GABAB receptors.
Aa, samples of a continuous whole-cell current-clamp recording from an SPN showing bath application of baclofen, induces membrane hyperpolarization associated with a decrease in neuronal input resistance. Subsequent application of 2-hydroxy-saclofen (2-OH-S) reduced the membrane response induced by baclofen. Ab, bath application of baclofen to another SPN induced membrane hyperpolarization corresponding with a decrease in neuronal input resistance. Subsequent bath application of CGP55845 reversibly reduced the magnitude of the membrane response to baclofen. B, summary histogram illustrating the pharmacological profile of GABAB receptor-mediated responses evoked in SPNs. The peak membrane potential responses (filled columns) and changes in neuronal input resistance (open columns) induced by GABAB receptor agonists and the effects of antagonists on agonist-induced responses are shown. Error bars represent s.e.m. Numbers above individual bars indicate number of cells tested (n). (*P < 0.01, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.03.)