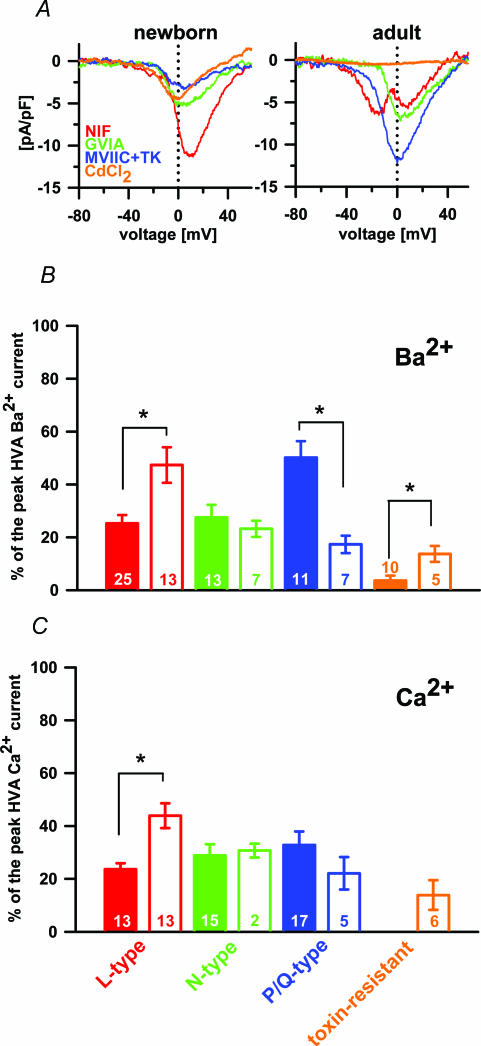
Figure 3. The separation of different VACCs in Ba2+ and Ca2+.
A, separated Ba2+ current densities through L-, N- and P/Q-type VACCs and toxin-resistant channels in newborn (left panel) and adult melanotrophs (right panel). Note the first peak in the nifedipine-sensitive current in adults is the LVA component and second peak the HVA component (red trace). B, the contribution of different VACC types to the peak HVA Ba2+ current: adult, filled bars; newborn, open bars. C, contribution of different VACC types to the peak HVA Ca2+ current: adult, filled bars; newborn, open bars. The toxin-resistant current was negligible in adult melanotrophs and was therefore not tested for statistical significance.